Types Of Ventilation - Air Alchemy Beyond The Breeze
Discover the diverse world of ventilation with insights into different types of ventilation. Explore natural and mechanical methods shaping indoor air quality. Learn how these systems contribute to healthier, more comfortable living environments.
Author:Rhyley CarneyReviewer:Paula M. GrahamNov 24, 202333.6K Shares467.5K Views

As we delve into the realm of types of ventilation, we navigate a landscape of diverse methods and systems designed to ensure optimal air circulation within enclosed spaces. Ventilation, a fundamental aspect of environmental engineering, plays a pivotal role in shaping the quality of indoor air.
Whether harnessing the forces of nature or employing sophisticated mechanical systems, understanding these types of ventilation is crucial for creating environments that promote health, comfort, and overall well-being.
What Is Ventilation?
Ventilation is a crucial component of environmental control, referring to the process of exchanging air within a space to maintain indoor air quality. It involves the circulation of fresh air while expelling stale or polluted air, contributing to the health and well-being of occupants.
Ventilation can occur through natural means, leveraging wind and temperature differentials, or through mechanical systems that utilize fans and ducts to control airflow.
Ventilation ensures a continuous flow of oxygen and the removal of pollutants, allergens, and excess moisture. Adequate ventilation is essential in both residential and commercial settings, as it not only supports respiratory health but also prevents the buildup of harmful substances.
Properly designed ventilation systems contribute to a comfortable and productive indoor environment, playing a pivotal role in creating spaces that are not only habitable but conducive to optimal living conditions.
Different forms of ventilation will be required depending on your building and its natural air supply to ensure a healthy breathing environment for residents. An operational ventilation system is actually needed by law in some circumstances, most notably in commercial and public buildings. As a result, before making an investment, it's a good idea to understand some of the many types of ventilation systems.
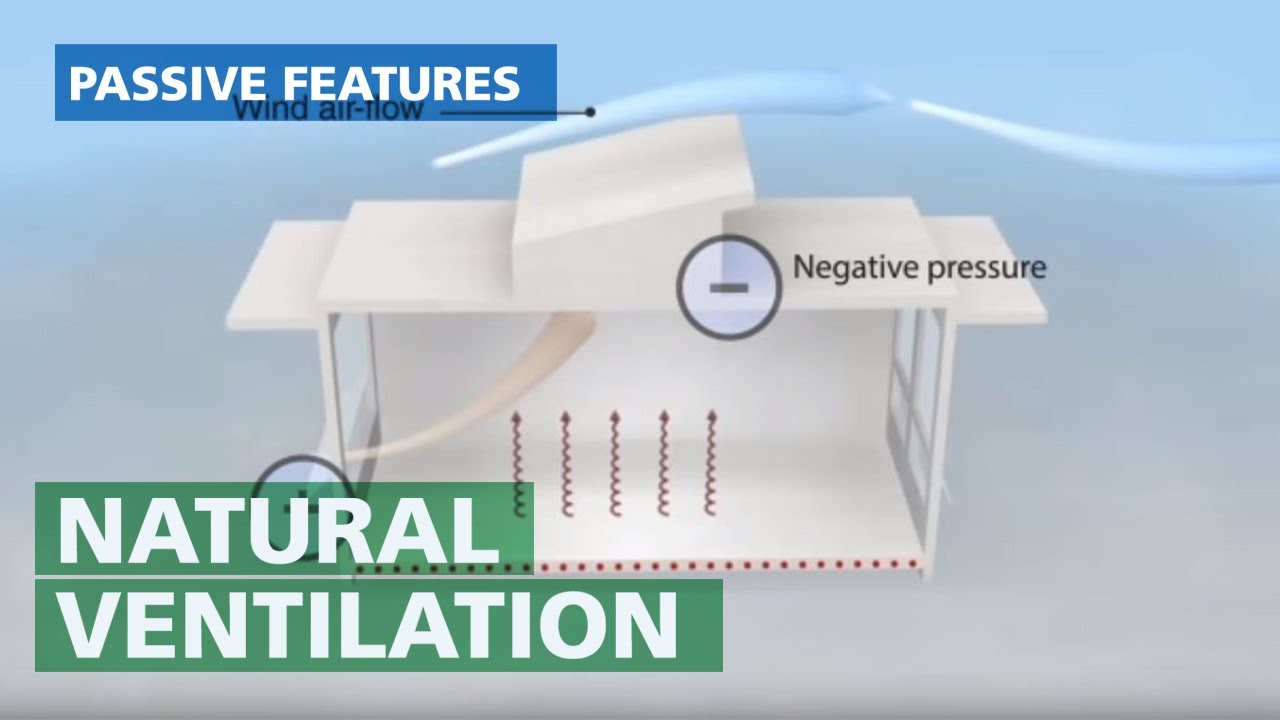
Natural Ventilation
Natural ventilation is a time-tested and sustainable method of refreshing indoor air by utilizing external forces such as wind and temperature differentials. This approach embraces the innate characteristics of the environment to facilitate a continuous and dynamic exchange of air within a space.
Unlike mechanical systems, natural ventilation relies on passive design elements like windows, doors, and vents strategically positioned to optimize airflow.
The primary mechanism involves the displacement of stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air, driven by natural phenomena. Wind forces and temperature gradients encourage the movement of air, creating a natural and energy-efficient ventilation system.
Natural ventilation not only reduces dependency on mechanical systems but also aligns with eco-friendly and cost-effective principles.
This method holds particular significance in sustainable architecture, promoting energy conservation and environmental harmony. Beyond its practical benefits, natural ventilation contributes to a more pleasant indoor atmosphere, fostering a connection between the occupants and the surrounding natural elements.
As societies increasingly prioritize eco-conscious living, natural ventilation stands as a timeless and effective solution for enhancing indoor air quality while minimizing the ecological footprint.
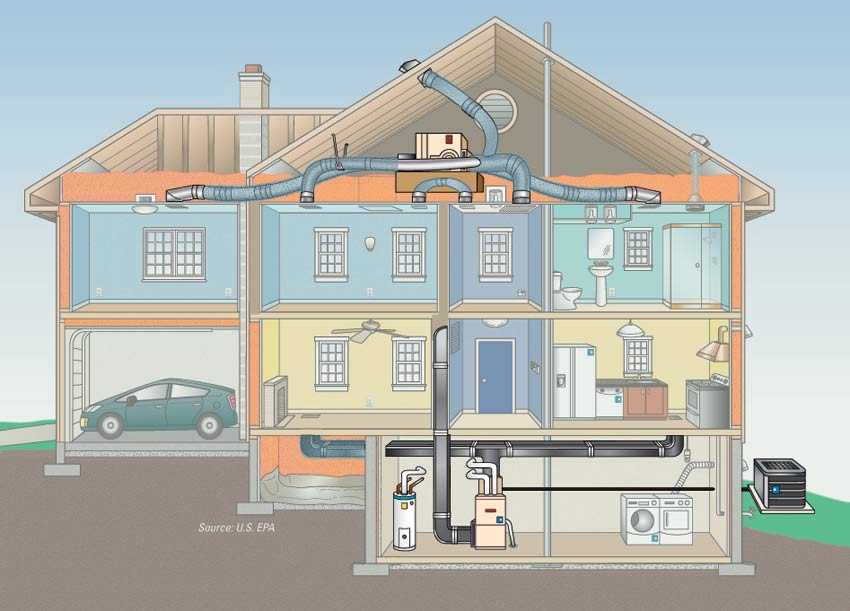
Mechanized Ventilation
Mechanized fan ventilation represents a technologically advanced approach to indoor air circulation, employing fans and mechanical systems to ensure precise and controlled airflow within enclosed spaces.
Unlike natural ventilation, which relies on environmental factors, mechanized fan systems provide a proactive and customizable solution for optimizing air quality and comfort.
The core of mechanized fan ventilation lies in the strategic placement of fans and ductwork to create a controlled airflow pattern. These systems are designed to address specific ventilation needs in spaces where natural ventilation may be insufficient.
High-efficiency fans, often equipped with variable speed controls, enable tailored adjustments to accommodate varying occupancy levels and environmental conditions.
One significant advantage of mechanized fan ventilation is its consistency and reliability. Regardless of external factors like wind or temperature, these systems deliver a steady and reliable supply of fresh air.
This makes them particularly valuable in buildings with complex structures or where natural ventilation may be impractical. As technology advances, mechanized fan ventilation systems continue to evolve, incorporating smart features and energy-efficient components.
This progress enhances not only the precision of airflow control but also the sustainability of these systems, contributing to a harmonious balance between environmental responsibility and optimal indoor air quality.
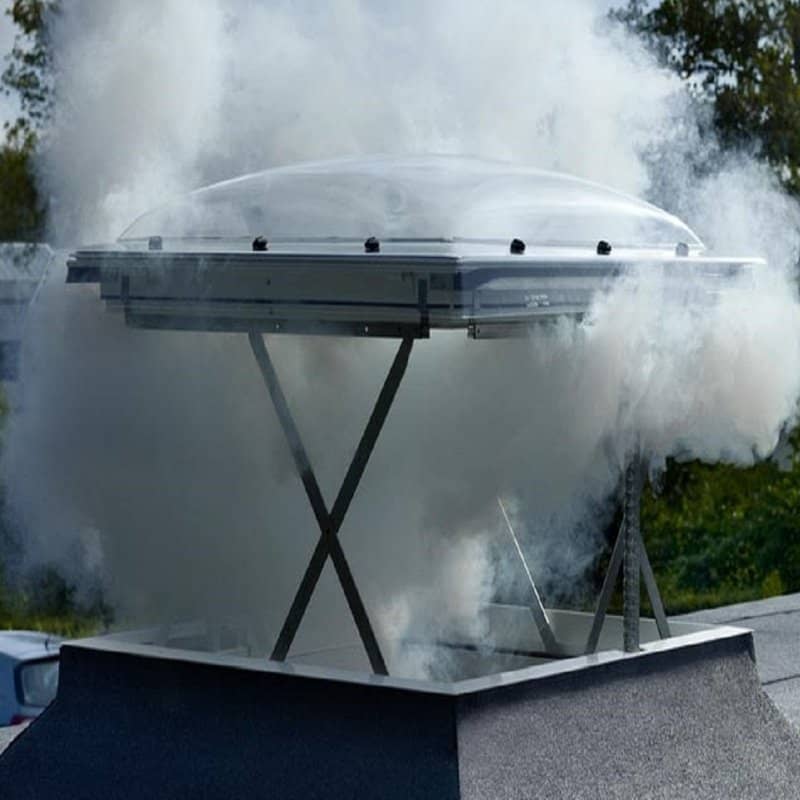
Smoke Ventilation
Smoke ventilation is a critical component of building safety systems, designed to manage the spread of smoke in the event of a fire. The primary objective is to create a safe and clear escape route for occupants while aiding firefighting efforts.
This specialized ventilation system operates distinctly from everyday ventilation, focusing on the rapid extraction of smoke to maintain visibility and reduce the risk of smoke inhalation.
In the event of a fire, smoke ventilation systems typically involve the use of mechanical devices such as smoke exhaust fans, vents, and dampers strategically placed to facilitate the efficient removal of smoke.
These systems play a crucial role in preventing the buildup of toxic gases and obscuring conditions, enabling occupants to evacuate quickly and emergency responders to navigate the premises effectively.
The design of smoke ventilation systems considers factors such as building layout, fire compartmentalization, and the location of potential fire sources. Automated controls and sensors ensure a swift response to detected smoke, activating the ventilation system promptly.
Smoke ventilation is an integral aspect of building safety, emphasizing the importance of rapid and effective smoke management in safeguarding lives and minimizing property damage during fire emergencies.
Supply Ventilation
Supply ventilation is a method of indoor air quality management that involves the controlled introduction of fresh outdoor air into a building, creating a positive pressure environment. This approach ensures a continuous supply of clean air, promoting a healthier and more comfortable indoor atmosphere.
The process typically involves the use of mechanical systems such as fans or blowers that draw in outdoor air and distribute it throughout the building.
Supply ventilation is distinct from exhaust ventilation, as it actively introduces fresh air rather than relying solely on the expulsion of stale indoor air. This method allows for greater control over air quality parameters such as temperature and humidity.
One of the key advantages of supply ventilation is its ability to mitigate indoor air pollutants and maintain optimal oxygen levels. This is especially beneficial in tightly sealed or energy-efficient buildings where natural air exchange may be limited.
By strategically placing supply vents, the system can ensure a uniform distribution of fresh air, preventing the stagnation of indoor pollutants and enhancing the overall comfort and well-being of occupants.
Exhaust Ventilation
Exhaust ventilation is a vital component of indoor air quality management, focusing on the expulsion of stale or contaminated air from enclosed spaces. This method relies on mechanical systems, such as fans or blowers, strategically placed to facilitate the efficient removal of indoor pollutants, odors, and excess moisture.
In exhaust ventilation systems, the primary goal is to create a negative pressure environment, encouraging the extraction of air from the building. This negative pressure prompts fresh outdoor air to naturally infiltrate the space through openings like windows and doors.
This method is particularly effective in spaces where indoor air quality is compromised, such as kitchens and bathrooms, where cooking odors and humidity can accumulate. Additionally, exhaust ventilation is commonly employed in industrial settings to remove fumes and contaminants.
Exhaust ventilation systems contribute significantly to maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment by preventing the buildup of pollutants. Regular air exchange enhances respiratory health, minimizes the risk of mold growth, and ensures a continuous flow of fresh air, creating spaces conducive to well-being and productivity.
Balanced Ventilation
Balanced ventilation is a comprehensive approach that seeks to maintain a harmonious equilibrium between incoming and outgoing air, ensuring a controlled exchange for optimal indoor air quality. This method combines elements of both supply and exhaust ventilation to create a balanced and energy-efficient system.
In a balanced ventilation system, the inflow of fresh outdoor air is matched with an equivalent outflow of stale indoor air. This equilibrium is achieved through the use of mechanical systems, such as heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) or energy recovery ventilators (ERVs).
These devices extract heat or coolness from the outgoing air and transfer it to the incoming fresh air, maximizing energy efficiency while ensuring a consistent flow of conditioned air.
This ventilation strategy is particularly advantageous in climates with extreme temperature variations. By recovering energy from the expelled air, balanced ventilation minimizes the energy load on heating and cooling systems, contributing to both comfort and energy savings.
Additionally, the controlled exchange of air helps manage humidity levels, prevents indoor air stagnation, and promotes a healthier living or working environment. Balanced ventilation stands as a holistic solution, striking a balance between energy efficiency and optimal indoor air quality.
Which Ventilation Systems Are The Most Energy-efficient?
Energy efficiency is an important factor in ventilation since ventilation systems can account for a large amount of a building's energy use. There are numerous ventilation systems to choose from, each with its own energy efficiency features.
Natural ventilation is the most energy-efficient because it does not require mechanical devices or energy inputs. It is driven by natural factors such as wind and temperature differences since it relies on air circulation through open windows or doors to exchange indoor air with outdoor air.
Mechanical ventilation systems, on the other hand, use fans, ducts, and vents to exchange indoor air with exterior air. These systems are fueled by electricity and can consume more energy, especially if not properly constructed or maintained.
- Using High-Efficiency Fans -High-efficiency fans can cut mechanical ventilation systems' energy usage by up to 50%.
- Sealing And Insulating Ducts- Leaky or poorly insulated ducts can drastically diminish mechanical ventilation systems' energy efficiency. Energy losses can be reduced by sealing and insulating the ducts.
- Using Occupancy Sensors -When the room is not in use, occupancy sensors can turn off the ventilation system, lowering energy consumption.
- Demand-Controlled Ventilation - One notable energy-efficient ventilation strategy is demand-controlled ventilation (DCV). This system utilizes sensors to monitor parameters like occupancy levels, temperature, and air quality.
- When areas are unoccupied, the ventilation rate decreases, conserving energy. As soon as occupancy is detected or air quality deteriorates, the system adjusts to ensure optimal ventilation. DCV is particularly effective in spaces with varying occupancy patterns, enhancing efficiency and contributing to substantial energy savings over time.
- Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) - Another key player in the realm of energy-efficient ventilation is Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV). This technology captures and recycles the heat from outgoing air, transferring it to the incoming fresh air.
- By preserving the energy that would otherwise be lost during the ventilation process, HRV systems maintain indoor temperature while reducing the load on heating and cooling systems. This dual-functionality makes HRV an integral part of sustainable building design.
- Integration Of Smart Technologies - Modern energy-efficient ventilation solutions often integrate smart technologies for enhanced control and automation. Smart ventilation systems can be programmed and monitored remotely, allowing users to optimize settings based on their preferences and changing environmental conditions.
This level of control not only increases user comfort but also ensures that energy is utilized efficiently, aligning with the broader goal of sustainable living.
Natural ventilation is the most energy-efficient because it consumes no electricity. There are, however, techniques to increase the energy efficiency of mechanical ventilation systems, such as utilizing high-efficiency fans, sealing and insulating ducts, and installing occupancy sensors.
As a result, it is critical to carefully analyze the energy efficiency of various ventilation systems and select the most appropriate one for the building's specific demands.
Types Of Ventilation - FAQs
How Does Natural Ventilation Work In Buildings?
Natural ventilation utilizes external forces like wind and temperature differences to facilitate airflow, promoting fresh air circulation.
What Are The Advantages Of Mechanical Ventilation?
Mechanical ventilation offers precise control over airflow, ensuring consistent air quality and temperature within a space.
Are There Energy-efficient Ventilation Options Available?
Yes, energy-efficient options like demand-controlled ventilation adjust airflow based on occupancy and air quality, optimizing energy usage.
How Can Ventilation Impact Indoor Air Quality?
Proper ventilation helps remove pollutants, allergens, and stale air, contributing significantly to improved indoor air quality.
Are There Smart Ventilation Solutions Available For Homes?
Yes, smart ventilation systems use sensors and automation to adapt airflow based on real-time conditions, enhancing efficiency and user comfort.
Conclusion
The exploration of the myriad types of ventilation underscores the dynamic interplay between design, technology, and the natural forces that govern air movement. From the simplicity of natural ventilation harnessing wind currents to the precision of mechanical systems driven by technological innovation, each approach contributes to the overarching goal of fostering spaces that are not just habitable but conducive to human health and productivity.
As we continue to advance in our understanding of ventilation, we pave the way for environments that strike an optimal balance between the outdoors and the controlled indoor spaces, ensuring a breath of fresh air in every sense.

Rhyley Carney
Author

Paula M. Graham
Reviewer
Latest Articles
Popular Articles