Top 9 Smart Contract Platforms In 2021
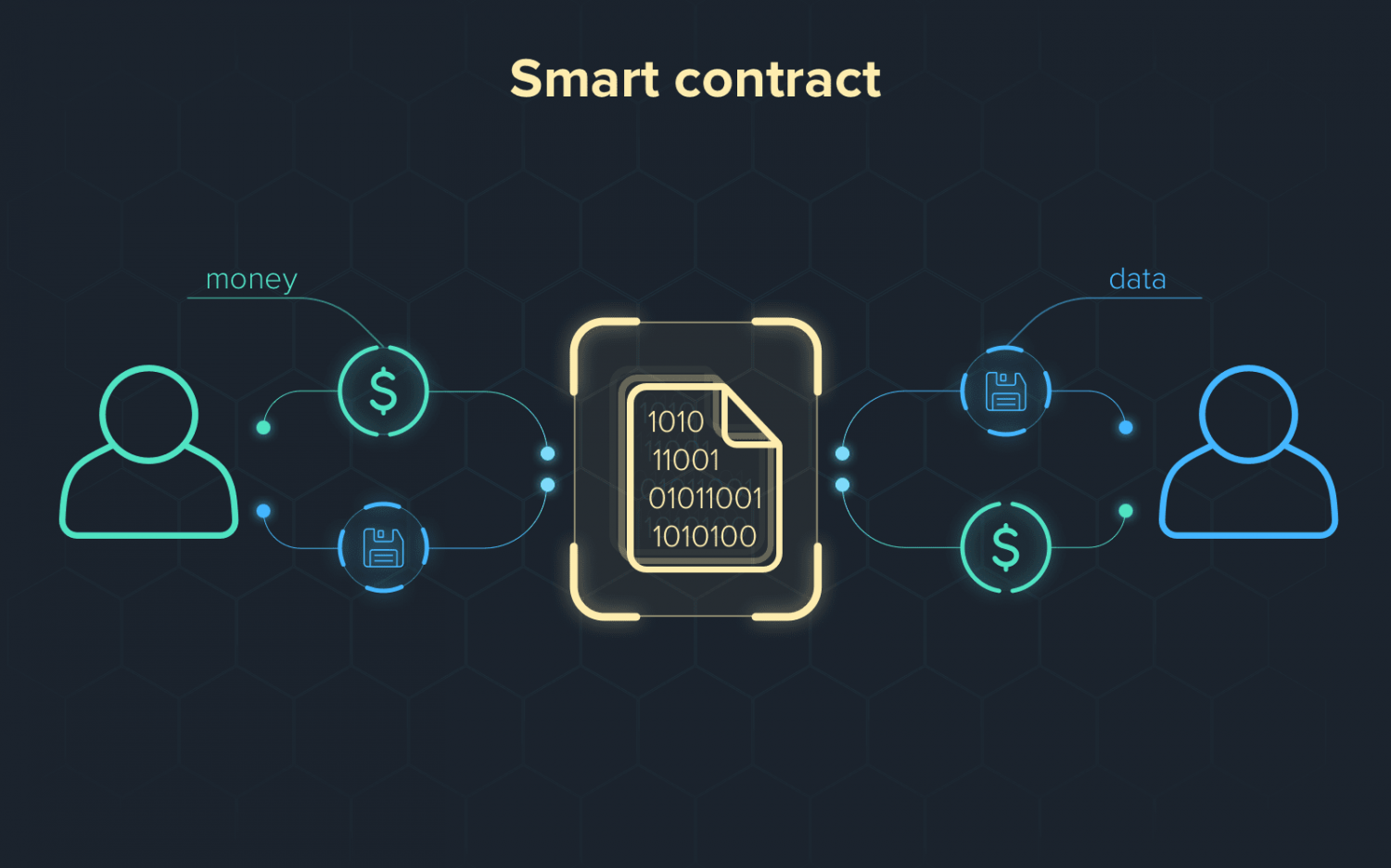
A smart contract is a self-executing contract in which the conditions of the buyer-seller agreement are put directly into lines of code. The code, as well as the agreements it contains, are disseminated throughout a decentralized blockchain network. Transactions are trackable and irreversible, and the programming regulates their execution.
Author:Camilo WoodReviewer:Stefano MclaughlinOct 06, 202197.6K Shares1.9M Views
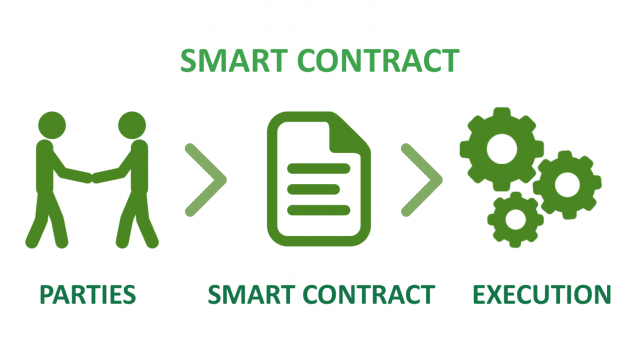
What Is A Smart Contract And How Does It Work?

What is a Smart Contract and What is it Used For?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract in which the conditions of the buyer-seller agreement are put directly into lines of code. The code, as well as the agreements it contains, are disseminated throughout a decentralized blockchain network. Transactions are trackable and irreversible, and the programming regulates their execution.
Nick Szabo, an American computer scientist who established a virtual currency dubbed "Bit Gold" in 1998, 10 years before the development of bitcoin, introduced smart contracts in 1994. In reality, Szabo is frequently mistaken for Satoshi Nakamoto, the anonymous creator of bitcoin, a claim he has refuted.
Smart contracts, according to Szabo, are automated transaction protocols that carry out the provisions of a contract. He sought to take electronic transaction methods like POS (point of sale) and bring them into the digital arena. Szabo also recommended the execution of a contract for synthetic assets like derivatives and bonds in his paper. Szabo stated: "These new securities are created in a variety of ways by mixing securities (such as bonds) and derivatives (such as options and futures). Due to computerized analysis of these complicated term structures, very complex payment term structures may now be constructed into standardized contracts and exchanged with low transaction costs."
In methods that predated blockchain technology, several of Szabo's predictions in the paper came true. Derivatives trading, for example, is now primarily done over computer networks with sophisticated term structures.
How Can Smart Contracts Be Enforced?
Smart contracts are enforced in the same manner as regular programs are enforced: the code is run by the computer, and the desired result is obtained.
Smart contracts are comparable to, but not identical to, real-world contracts. In the real world, if I breach a contract with another person, I have the option of taking them to court to have the problem resolved. There is no court for smart contracts. Instead, they use pre-defined rules that participants create and then execute on the blockchain.
The regulations do not change once they have been executed. Participants can withdraw funds from their account if the contract allows it. They can't if it wasn't created for this reason. Here's an easy example: Let’s say I’m taking part in the VariabL alpha, a decentralized exchange. By executing a 2X/4X Long or 2X/4x Short ‘contract,' I can bet on the future price of Ethereum. I must wait 72 hours after signing the contract before receiving payment. What if I wanted to sell my contract before the end of the term? Or do you want to take an 8X short position? I'm afraid I won't be able to. Why? This is because the smart contract forbids it. I can re-configure the code and post another contract on the blockchain if I want to change the contract's terms, but that code will then become "the rule." It will carry out its commands to the letter.
What Are Examples Of Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts can be applied in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, supply chain management, and financial services. The following are some examples:
Government Voting System
By providing a safe environment, smart contracts make it more difficult to manipulate the voting system Smart contract votes would be ledger-protected, making them very difficult to interpret.
Furthermore, smart contracts have the potential to raise voter turnout, which has historically been low due to an inefficient system that requires voters to queue, show identification, and fill out paperwork. Voting can expand the number of participants in a voting system when it is transferred online using smart contracts.
Healthcare
With a private key, blockchain can store patients' encoded health records. Due to privacy considerations, only particular individuals would have access to the records. Similarly, smart contracts can be used to conduct research in a private and secure manner.
All patient hospital receipts can be kept on the blockchain and shared with insurance providers automatically as proof of service. Furthermore, the ledger can be used for a variety of tasks, including supply management, drug supervision, and regulatory compliance.
Supply Chain
Paper-based systems, in which forms are routed through many channels for approval, have historically harmed supply chains. The time-consuming procedure raises the danger of fraud and loss.
By providing parties involved in the chain with an accessible and secure digital version, blockchain can eliminate such concerns. Smart contracts can be used for inventory management as well as payment and task automation.
Financial Services
In a variety of ways, smart contracts assist in the transformation of traditional financial services. When it comes to insurance claims, they verify for errors, route them, and then send funds to the user if everything checks up.
Smart contracts include essential bookkeeping capabilities and eliminate the chance of accounting records being tampered with. They also allow shareholders to participate in transparent decision-making. They also assist in trade clearing, which is the process of transferring payments after the amounts of trade settlements have been computed.
What Are Some Of The Benefits Of Smart Contracts
Because smart contracts are often put on and protected by blockchain, they have the advantages of lowering transaction risk, lowering management and service costs, and boosting business process efficiency when compared to traditional contracts.
Autonomy And Savings
Smart contracts decrease the possibility of third-party manipulation by eliminating the requirement for brokers or other intermediaries to ratify the agreement. Furthermore, the lack of an intermediary in smart contracts saves money.
Backup
All documents kept on the blockchain are duplicated many times, allowing for the restoration of originals in the event of data loss.
Safety
Smart contracts are encrypted, and cryptography protects all papers from being tampered with.
Speed
Smart contracts use computer protocols to automate actions, saving hours of time in various commercial processes.
Accuracy
Smart contracts eliminate errors that occur as a result of manual filling out of several forms.
Limitations Of Smart Contracts
Difficult To Change
It's nearly impossible to change smart contract operations, and any programming fault can be time-consuming and costly to fix.
Probability Of Loopholes
According to the concept of good faith, parties will deal fairly and not get benefits unethically from a contract. However, using smart contracts makes it difficult to ensure that the terms are met according to what was agreed upon.
Third Party
Although smart contracts seek to eliminate third-party involvement, it is not possible to eliminate them. Third parties assume different roles from the ones they take in traditional contracts. For example, lawyers will not be needed to prepare individual contracts; however, they will be needed by developers to understand the terms to create codes for smart contracts.
Vague Terms
Since contracts include terms that are not always understood, smart contracts are not always able to handle terms and conditions that are vague.
The Top 9 Smart Contract Platforms In 2021
According to Alex-Paul Manders, director of Information Services Group, an IT advisory firm, the emergence of blockchain platforms has raised awareness of decentralized finance, or DeFi, as a means of creating new business models that threaten traditional banking, finance, and supply chain financing. Blockchain platforms, according to Manders, have the potential to disrupt old supply chain enterprises and technology processes. Pharmaceutical businesses, for example, must track and trace products and materials in the United States, which necessitates a new approach for supply chain members to communicate and transact data more efficiently and transparently than previously necessary. Blockchain technology may be the solution.
R3 Corda, Hyperledger, and Ethereum are the top three blockchain frameworks for these use cases, according to Menon, with EOSIO and Quorum gaining traction.
Here are nine of the most popular blockchain platforms.
Ethereum
Ethereum is one of the oldest and most well-known blockchain technologies, having been launched in 2013. It offers a genuinely decentralized blockchain network that is comparable to the Bitcoin network. Its primary strength, according to Manders, is that it allows for real decentralization while still supporting smart contracts. Slow processing times and greater transaction processing charges are two of its major flaws when compared to competing platforms. It has its own cryptocurrency, ether, in addition to its role as a blockchain platform that enables enterprise apps.
Technologists who create decentralized apps, or dApps, on the Ethereum network are rapidly adopting the Ethereum platform. For nonfungible tokens (NFTs), a sort of digital asset that can be traded on a blockchain, there is a slew of platforms and exchanges to choose from. It has a well-developed ecosystem of tools for building smart contracts in the Solidity programming language, which is executed on the Ethereum Virtual Machine. Alternative blockchain networks, on the other hand, can execute transactions faster and at a cheaper cost than Ethereum, but many observers believe this will change once Ethereum implements a more efficient security mechanism. It also boasts a vibrant development community led by the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance, which includes Intel, JPMorgan, and Microsoft among its more than 250 members.
IBM Blockchain
According to Manders, IBM Blockchain is a private, decentralized blockchain network that has been most effective with commercial clients who are less risk-averse. He sees the greatest potential in connecting it to enterprise cloud and legacy systems more seamlessly than other decentralized networks.
The IBM Blockchain developer tool was built with flexibility, functionality, and customization in mind. IBM has also put effort into developing a user-friendly interface to make important processes like setting up, testing, and quickly deploying smart contracts easier. IBM's head of blockchain solutions development, Rakesh Mohan, claimed the business has made great progress in financial services and banking, as well as supply chain. IBM Food Trust, which has performed over 18 million transactions representing over 17,000 goods, and the Blockchain Community Initiative in Thailand, which offers services such as payment obligations and business auctions for 22 Thai banks, are two examples of successful blockchain apps.
Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric is a set of tools developed by IBM and The Linux Foundation to aid in the development of blockchain applications. It was designed with enterprise distributed ledger applications in mind from the start. It features a diverse ecosystem of components that can be combined to form a modular design. It performs well in closed blockchain implementations, increasing security and speed. It also has an open smart contract model that supports a variety of data types, including account and unspent transaction output, as well as UTXO models. By isolating transactions in channels or facilitating the exchange of private data in private data collections on a need-to-know basis, Hyperledger Fabric can also increase data privacy. According to its proponents, it also enables high-speed transactions with low finality and confirmation delay.
The latest advances, according to Arnaud Le Hors, a senior technical staff member of blockchain and web open technologies at IBM who also leads the Hyperledger Technical Steering Committee, allow an organization to join a channel without having to duplicate the entire history of the ledger. This allows for a faster startup time and reduced storage space. Hyperledger Fabric has a vibrant and diverse community working on new features such as consensus methods, more privacy options for GDPR compliance, and operational enhancements.
Hyperledger Sawtooth
Hyperledger Sawtooth, another open-source blockchain project co-founded by Hyperledger and the Linux Foundation, employs a novel consensus mechanism known as Proof of Elapsed Time, which can be used in conjunction with hardware-based security technologies to allow "trusted execution environments" of program code to run in secure enclaves, which are secure areas of computer memory. The most typical applications, according to Shawn Amundson, CTO of Bitwise IO and Hyperledger Sawtooth maintainer, include constructing supply chain systems and adapting Sawtooth for specialized reasons, such as new consensus algorithms.
A Sawtooth Library is being developed, which will allow developers of custom distributed ledgers to pick and choose whatever parts of Sawtooth to employ in their applications. Sawtooth is also implementing Splinter for networking, which will allow dynamic private circuits (groups of nodes); Hyperledger Transact for transaction processing, which will improve smart contract capabilities; and Augrim for consensus, which will increase the number of supported algorithms.
R3 Corda
R3 Corda is being debated as a blockchain or a different form of a distributed ledger. It employs a new consensus process in which transactions are cryptographically linked but does not group many transactions into a block on a regular basis. "Both a blockchain and not a blockchain," according to the official Corda website. One of the main advantages of this method is that all transactions are handled in real-time, which might increase performance when compared to other blockchains.
Corda provides an appealing approach for financial transactions and smart contracts with high security, and the R3 consortium has a large following in the financial industry. Bank of America, HSBC, Intel, and Microsoft are among the most vocal supporters.
Corda, according to Manders, has a good chance of becoming the de facto network for insurance transaction processing. Other federated blockchain networks, on the other hand, can process transactions faster and for less money.
Tezos
Tezos is an older platform that allows decentralized applications, smart contracts, and innovative financial instruments like NFTs, which can be considered of as a modern version of trading cards that are coupled to digital assets. It has been in development since 2014. The platform has a dynamically upgradeable protocol as well as modular software clients that allow it to adapt to new applications. The Tezos community has been rapidly developing the platform, with recent improvements that have improved performance and extended the smart contract size limit.
EOSIO
In 2018, the EOSIO blockchain platform was released as an open-source project for the first time. It is well-suited to the creation of decentralized applications and smart contracts. According to its proponents, it uses a complicated consensus process based on PoS that gives higher performance than earlier systems like Ethereum. It also contains support for a governance feature that allows users to vote on platform updates.
Fast transactions and advanced account permission features for installing applications are key strengths. The platform has over 400 applications, including identity management, supply chain management, and gaming.
Stellar
Stellar is a more recent blockchain platform that is well-suited to a variety of decentralized finance applications. As a result of the implementation of the Stellar Consensus Protocol, transactions on a public blockchain network are supposed to be processed and finalized more quickly. It also incorporates security methods for preventing rogue or suspicious parties from participating in a financial transaction. Several companies have used it for international trade and cross-border money exchange.
Quorum
JPMorgan's Quorum is a customized version of Ethereum developed by the financial services firm. It takes the Ethereum blockchain platform's basic work and repackages it into a secure environment suitable for banks. It has been optimized to facilitate high-speed transactions on a private network between organizations like banks and insurance companies. It also improves Ethereum's privacy features in order to comply with requirements such as the GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in California.

Camilo Wood
Author

Stefano Mclaughlin
Reviewer
Latest Articles
Popular Articles