HSA Vs HMO - Which Plan Is Best For You?
Uncover the key differences between HSA vs HMO health insurance plans and discover which one is best suited for your healthcare needs and budget.
Author:Katharine TateReviewer:Karan EmeryNov 16, 20235.2K Shares70.5K Views

Take control of your healthcare expenses with our expert analysis of HSA vs HMO plans. Understand the impact of deductibles, copays, and out-of-pocket costs on your financial well-being.
In today's complex healthcare landscape, making the right choices about your medical coverage is more critical than ever. Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) represent two distinct options that individuals and families often consider when it comes to managing their healthcare expenses. While both are popular choices, they operate on different principles and serve various needs.
Choosing the right healthcare plan is not just a financial decision but a choice that can significantly impact the quality of care you receive and the ease with which you access it. It can determine whether you have the freedom to select your healthcare providers or are part of a managed care network. Moreover, it affects the extent to which you can proactively save and plan for your healthcare expenses. In this article, we will delve into the world of HSAs and HMOs, offering a comprehensive comparison to help you navigate the complexities of these healthcare options. We will explore their fundamental features, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and the factors you should consider when making a decision that aligns with your unique healthcare needs.
HMOs and HSAs have gained popularity for distinct reasons. HMOs are known for their affordability, often featuring lower premiums and predictable out-of-pocket costs. On the other hand, HSAs have become a favorite for those who value flexibility and want to save money while enjoying tax benefits.
Delving Into HSAs - Health Savings Accounts For Healthcare Savings
An HSA is a tax-advantaged savings account that allows you to set aside money to pay for qualified medical expenses. You can contribute to an HSA pre-tax, which means you can deduct your contributions from your taxable income. This can save you money on taxes.
Unveiling The Tax Advantages Of HSAs
HSAs provide a unique opportunity to save for future healthcare expenses while enjoying significant tax benefits. Here's how you can reap the full tax advantages of HSAs:
Tax-Deductible Contributions
You can deduct your HSA contributions from your taxable income, reducing your tax burden. This means that every dollar you contribute to your HSA is actually costing you less than a dollar because you're saving on taxes.
Tax-Deferred Growth
The funds you contribute to your HSA have the potential to grow tax-deferred, meaning you won't pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw them. This allows your HSA to accumulate value over time, providing a larger pool of money to cover future healthcare expenses.
Tax-Free Withdrawals
Withdrawals from your HSA for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. This includes expenses such as deductibles, copayments, prescriptions, vision care, and dental care. When you use your HSA funds to pay for these expenses, you're essentially using pre-tax dollars, which is a significant tax savings.
Maximizing HSA Contributions For Future Healthcare Needs
To maximize the benefits of your HSA, it's important to contribute as much as you can afford. The maximum HSA contribution limits for 2023 are $3,850 for individuals and $7,750 for families. If you're high-earner, you may be able to contribute even more through catch-up contributions.
Here are some strategies for maximizing your HSA contributions:
- Set up automatic payroll deductions -This ensures that you're consistently contributing to your HSA and that you don't miss out on any tax benefits.
- Consider making a lump-sum contribution at the beginning of the year -This can give your HSA more time to grow tax-deferred.
- Contribute as much as you can comfortably afford -Remember, you can always adjust your contributions later if your financial situation changes.
Utilizing HSAs To Cover Qualified Medical Expenses
HSA funds can be used to pay for a wide range of qualified medical expenses. This includes expenses such as:
- Deductibles -The amount you have to pay out of pocket before your insurance starts to cover your medical expenses.
- Copayments -Fixed dollar amounts you pay for specific healthcare services, such as doctor's visits or prescription drugs.
- Out-of-pocket prescription drug costs -The amount you pay for prescription drugs after your insurance has paid its share.
- Vision care -Exams, glasses, and contact lenses.
- Dental care -Exams, cleanings, fillings, and other dental procedures.
You can use your HSA funds to pay for these expenses by using an HSA debit card or by submitting receipts to your HSA administrator for reimbursement.
By taking advantage of the tax benefits and flexibility of HSAs, you can effectively save for future healthcare expenses and reduce your overall healthcare costs. HSAs offer a valuable tool for managing your healthcare finances and ensuring that you're prepared for future medical needs.
HMOs - Health Maintenance Organizations For Network-Based Care
HMOs, or Health Maintenance Organizations, are a type of managed care health insurance plan that emphasizes preventive care and limits access to out-of-network providers. In exchange for lower premiums, HMO members agree to receive most of their medical care from within the plan's network of providers, which typically includes hospitals, doctors, and other healthcare professionals.
Navigating The In-Network Provider Network Of HMOs
HMOs maintain a network of healthcare providers with whom they have negotiated contracted rates for services. This network may include hospitals, doctors, specialists, and other healthcare professionals. To receive in-network coverage, HMO members must choose a primary care physician (PCP) from the plan's network. The PCP coordinates the member's care and refers them to specialists within the network when necessary.
When choosing an in-network provider, it's important to consider factors such as:
- Location -Choose providers who are conveniently located near your home or work.
- Specialization -Select providers who have expertise in treating the conditions or concerns you have.
- Experience and reputation -Check provider credentials and read patient reviews to assess their experience and reputation.
- Language proficiency -If language is a barrier, ensure that the provider speaks your preferred language or has access to an interpreter.
Understanding The Role Of Primary Care Physicians In HMOs
In an HMO, your primary care physician (PCP) plays a central role in managing your healthcare. Your PCP will be your first point of contact for most medical needs, providing routine care, preventive screenings, and treatment for common illnesses. They will also refer you to specialists within the HMO network if you need more specialized care.
Out-of-Network Care Considerations For HMOs
HMOs typically limit coverage to providers within their network. If you receive care from an out-of-network provider, you may have to pay the full cost of the care yourself, or your insurance may cover only a small portion of the cost. There are some exceptions to this rule, such as emergency care.
Here are some things to consider when it comes to out-of-network care with an HMO:
- Understand the plan's out-of-network coverage -Before receiving care from an out-of-network provider, check with your HMO to understand what, if any, coverage you will have for the care.
- Get pre-authorization for non-emergency care -If you need non-emergency care from an out-of-network provider, you may need to get pre-authorization from your HMO. This means that you will need to get approval from the HMO before receiving the care, and the HMO will decide whether to cover the care and how much it will pay.
- Be prepared to pay more for out-of-network care -Out-of-network care typically costs more than in-network care. Be prepared to pay a higher deductible, copays, or coinsurance for out-of-network care.
HMOs offer a cost-effective way to manage your healthcare by limiting access to out-of-network providers. However, it's important to understand the plan's network and out-of-network coverage before you choose an HMO.
Deciphering The Key Differences - HMO Vs HSA
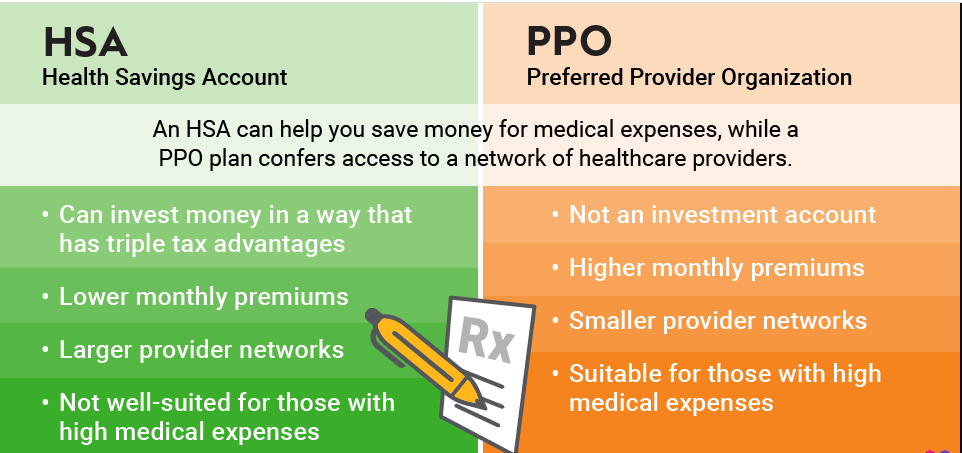
When making decisions about your healthcare coverage, it's crucial to understand the key differences between HSA and HMO plans to determine which one best suits your needs and preferences. One of the most significant distinctions between HSAs and HMOs lies in their cost structure, particularly in terms of premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket expenses.
HSA Premiums - Lower Premiums For Higher Deductibles
HSAs typically have lower monthly premiums compared to HMO plans. This is because HSAs are paired with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs), meaning you have to pay a higher amount out of pocket before your insurance starts to cover your medical expenses. This higher deductible translates to lower premiums.
HMO Premiums - Higher Premiums For Lower Deductibles
On the other hand, HMO plans typically have higher monthly premiums compared to HSAs. This is because HMOs have lower deductibles, meaning you start paying your insurance's share of medical expenses sooner. The lower deductible leads to higher premiums.
Deductibles And Out-of-Pocket Expenses In HSAs And HMOs
The deductible is the amount you have to pay out of pocket for covered medical expenses before your insurance starts to pay. Once you meet your deductible, your insurance will start covering a portion of your medical expenses, typically a percentage or a fixed amount per service.
Out-of-pocket expenses are the total amount you pay for covered medical expenses, including your deductible, copayments, and coinsurance. Copayments are fixed dollar amounts you pay for specific healthcare services, such as doctor's visits or prescription drugs. Coinsurance is a percentage of the cost of covered medical services that you pay after your insurance has paid its share.
In general, HSAs have higher deductibles and lower out-of-pocket expenses compared to HMOs. This is because HSA members are expected to pay more out of pocket before their insurance starts covering expenses, but they also have the opportunity to save money through tax-advantaged HSA contributions.
HMO members typically have lower deductibles and higher out-of-pocket expenses compared to HSA members. This is because HMO members start paying their insurance's share of expenses sooner, but they may also have higher copayments and coinsurance.
Network Restrictions - In-Network Vs. Out-of-Network Care
One of the primary distinctions between HSAs and HMOs lies in their network restrictions. HSAs offer broad care options with no network restrictions, while HMOs focus on network-based care to control expenses.
HSAs - No Network Restrictions For Broad Care Options
HSAs are not tied to a specific network of providers, unlike HMOs. This means that HSA members have the flexibility to choose healthcare providers from any network, including in-network, out-of-network, and even those participating in different insurance plans. This flexibility allows HSA members to seek care from providers they trust and have experience with, regardless of their network affiliation.
HMOs - Network-Based Care For Controlled Expenses
HMOs, on the other hand, operate within a defined network of contracted providers. This network includes hospitals, doctors, specialists, and other healthcare professionals who have agreed to provide services at discounted rates to HMO members. By limiting care to in-network providers, HMOs can control costs and ensure that enrollees receive coordinated care.
Out-of-Network Care Costs And Considerations
While HSAs offer the freedom to choose any provider, HMOs typically require pre-authorization for out-of-network care. If you receive out-of-network care without pre-authorization, you may have to pay the full cost of the service. Even with pre-authorization, out-of-network care may be more expensive than in-network care.
When considering an HMO, it's important to assess the adequacy of the in-network provider network. Ensure that the plan includes providers for your specialty needs and that the network is conveniently located. If you anticipate needing out-of-network care, understand the potential costs and authorization requirements.
Tax Benefits - HSA-Specific Advantages
HSAs stand out from HMOs in their unique tax advantages. HSAs offer triple tax benefits: pre-tax contributions, tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses, and tax-deferred investment growth.
Pre-Tax HSA Contributions For Reduced Taxable Income
HSA contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, meaning they reduce your taxable income. This can lower your tax liability and save you money each year. For example, if you contribute $3,000 to your HSA and your tax bracket is 22%, you effectively save $660 in taxes.
Tax-Free Withdrawals For Qualified Medical Expenses
Withdrawals from your HSA to pay for qualified medical expenses, such as deductibles, copayments, and prescriptions, are tax-free. This means that you don't have to pay taxes on the money you withdraw to cover your healthcare costs.
Tax-Deferred Investment Growth For Long-Term Savings
The funds in your HSA have the potential to grow tax-deferred, meaning you won't pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw them. This allows your HSA to accumulate value over time, providing a larger pool of money to cover future healthcare expenses.
The tax benefits of HSAs can significantly enhance their overall value, making them an attractive option for those who want to save for healthcare expenses while enjoying tax savings.
Making An Informed Choice - HSA Vs HMO
Deciding between an HSA and an HMO plan requires careful consideration of your individual needs, healthcare utilization patterns, and financial circumstances. Here's a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed choice:
Assessing Individual Needs And Healthcare Utilization
Your age, health status, and family medical history play a crucial role in determining the most suitable healthcare plan for you. If you are young and generally healthy, with a low likelihood of requiring frequent medical care, an HSA may be a good choice due to its lower monthly premiums and broader network options. However, if you have an ongoing chronic condition or a family history of health issues, an HMO may be more appropriate as it can provide more predictable and controlled healthcare costs.
Evaluating Expected Healthcare Usage Patterns
Analyze your past healthcare usage patterns and consider your anticipated need for medical services. If you typically have low healthcare expenses, an HSA can be a cost-effective option, allowing you to accumulate tax-advantaged savings for future medical needs. However, if you expect to use healthcare services frequently, an HMO's lower out-of-pocket costs due to its network restrictions may be more beneficial.
Balancing Cost Savings And Access To Care
Weigh the potential cost savings of different plans against the importance of having access to a wide range of healthcare providers. HSAs offer lower premiums and broader network options, but you may incur higher out-of-pocket costs if you use out-of-network providers. HMOs have higher premiums but lower out-of-pocket costs for in-network care, but you may have limited access to specific providers or specialty care.
Budgeting For Healthcare Expenses
Factor in the monthly premiums and deductibles associated with each plan. HSAs typically have lower monthly premiums but higher deductibles, while HMOs generally have higher premiums but lower deductibles. Consider your monthly budget and ability to pay a higher deductible when making a choice.
Anticipating Out-of-Pocket Expenses And Copays
Estimate potential out-of-pocket expenses, including copayments and coinsurance, for each plan. HSAs may have higher out-of-pocket costs if you use out-of-network providers, while HMOs may have lower out-of-pocket costs for in-network care. Evaluate your risk tolerance and ability to cover higher out-of-pocket expenses.
Planning For Unexpected Medical Costs
Consider the potential for unexpected medical costs and how each plan would handle them. HSAs provide a larger pool of funds to cover unexpected expenses, while HMOs may limit coverage for certain services or require pre-authorization. Assess your financial situation and ability to handle unexpected medical costs.
Prioritizing Choice In Healthcare Providers
HSAs offer the flexibility to choose any healthcare provider, including in-network, out-of-network, and even those participating in different insurance plans. This flexibility allows you to seek care from providers you trust and have experience with, regardless of their network affiliation.
Appreciating The Cost-Control Benefits Of HMOs
HMOs provide cost-control benefits by limiting care to in-network providers. This can result in lower out-of-pocket costs for routine care and predictable healthcare expenses. If you prefer predictable expenses and value the cost-control aspect, an HMO may be a good choice.
Finding The Right Balance Between Choice And Cost
Ultimately, the decision between an HSA and an HMO depends on your individual needs, preferences, and financial situation. Consider your age, health status, expected healthcare usage patterns, budget, and priority for choice in healthcare providers. Weigh the cost savings, access to care, and flexibility offered by each plan to make an informed decision that aligns with your healthcare needs.
Frequently Asked Questions - Hsa Vs Hmo
What Happens To An HSA If You Switch To An HMO?
When you switch to an HMO, your HSA remains yours and you can continue to use it to pay for qualified medical expenses. However, you will no longer be able to contribute to your HSA unless you have a high-deductible health plan (HDHP).
What Happens To My HSA If I Cancel My Insurance?
If you cancel your health insurance, you will still have access to your HSA funds and can continue to use them to pay for qualified medical expenses. However, you will no longer be able to make contributions to your HSA.
Can I Have Both An HMO And An HSA?
It is possible to have an HSA alongside a high-deductible health insurance plan, but having both an HMO and an HSA simultaneously is uncommon as HMOs usually have different coverage and provider network requirements.
Conclusion
In the choice between HMO vs HSA, it all boils down to your individual healthcare needs and financial circumstances. HMOs offer cost predictability and a structured approach to care, making them a solid option for those who prioritize affordability and preventive services. On the other hand, HSAs provide flexibility, tax advantages, and the opportunity to build long-term savings, making them an appealing choice for those who want more control over their healthcare decisions.
The key takeaway is that there's no one-size-fits-all answer in the HMO vs HSA debate. Your decision should be a well-informed one, driven by your personal preferences, budget, and healthcare requirements. Take the time to assess your needs, weigh the pros and cons, and consider the advice of healthcare professionals when making your choice. By doing so, you can ensure that your healthcare plan aligns with your unique situation, providing you and your family with the best possible care and financial security.

Katharine Tate
Author

Karan Emery
Reviewer
Latest Articles
Popular Articles