Financial Inclusion Initiatives - Definition, Examples, And Why It's Important
Unlocking Financial Freedom - Explore groundbreaking financial inclusion initiatives that are reshaping the future. From empowering the unbanked to fostering economic growth.
Author:Luqman JacksonReviewer:Liam EvansJan 17, 20243.2K Shares53.8K Views

Embark on a transformative journey towards global economic empowerment with our spotlight on cutting-edge financial inclusion initiatives. In a world where financial access is synonymous with opportunity, these initiatives are pioneering pathways for the unbanked and underserved communities.
Witness the power of inclusive banking models, innovative digital solutions, and impactful policies that bridge the gap, bringing financial services to the doorstep of those long excluded from the economic mainstream.
Immerse yourself in the stories of lives changed, businesses flourishing, and communities thriving as we delve into the heart of financial inclusion. From microfinance revolutions to groundbreaking fintech innovations, explore how these initiatives are not just opening bank accounts but unlocking the true potential of individuals and societies.
What Is Financial Inclusion?
Financial inclusionis all about ensuring everyone has access to affordable and useful financial services, regardless of their income, background, or location. This includes essential services like:
1. Transactions and payments -This means having a safe and reliable way to store money, send and receive payments, and make purchases.
2. Savings accounts -A safe place to grow your money and plan for the future.
3. Credit -Borrowing money for necessary expenses or starting a business.
4. Insurance -Protecting yourself and your loved ones from financial risks like illness, accidents, or loss of income.
Factors Of Financial Inclusion
The determinant factors of the main indicator of financial inclusion are formal account, formal saving, and formal credit. The determinant factors of financial inclusion are:
- Income
- education
- age
- gender
Why Is Financial Inclusion Important?
1. Reduces poverty and inequality -When people have access to financial tools, they can better manage their money, invest in their businesses, and build assets. This leads to greater economic security and overall well-being.
2. Empowers individuals and communities -Financial inclusion gives people control over their finances and makes them more resilient to shocks and emergencies. It also unlocks opportunities for starting businesses, improving education, and investing in health.
3. Boosts economic growth -A financially included population contributes more to the economy through increased savings, investment, and entrepreneurship. This leads to job creation, higher incomes, and improved living standards for everyone.
How Is Financial Inclusion Achieved?
- Government policies -Setting regulations that favor financial inclusion, promoting financial literacy, and supporting microfinance initiatives.
- Technology -Leveraging digital technologies like mobile banking and online platforms to reach unbanked populations and offer affordable services.
- Financial institutions -Developing products and services tailored to the needs of low-income individuals and underserved communities.
- Non-profit organizations -Providing financial education, offering financial products and services directly, and advocating for policies that promote inclusion.
Examples Of Financial Inclusion Initiatives
Here are three diverse examples of successful financial inclusion initiatives, showcasing different approaches and impacts:
1. M-Pesa In Kenya
- Type -Mobile money platform.
- Challenge -Lack of access to traditional banking services in rural areas.
- Solution -M-Pesa allows secure and convenient money transfers, payments, and savings via mobile phones.
- Impact -Revolutionized financial access for millions of Kenyans, empowering individuals and boosting economic activity.
- Key takeaway -Technology can provide innovative solutions for remote areas and unbanked populations.
2. Jan Dhan Yojana In India
- Type -Government-led scheme with banks.
- Challenge -Wide unbanked population with limited financial access.
- Solution -Opened over 400 million bank accounts, offering basic financial services and access to government benefits.
- Impact -Significantly increased financial inclusion and social welfare program reach, empowering individuals and fostering financial security.
- Key takeaway -Government collaboration with financial institutions can drive large-scale financial inclusion.
3. CGD In Brazil
- Type -Social bank focused on underserved communities.
- Challenge -Limited access to affordable financial services for low-income populations.
- Solution -Offers microloans, savings accounts, and financial education programs with flexible terms and community outreach.
- Impact -Empowers low-income families to start businesses, manage finances, and improve their livelihoods.
- Key takeaway - tailored services and community engagement can address the specific needs of marginalized groups.
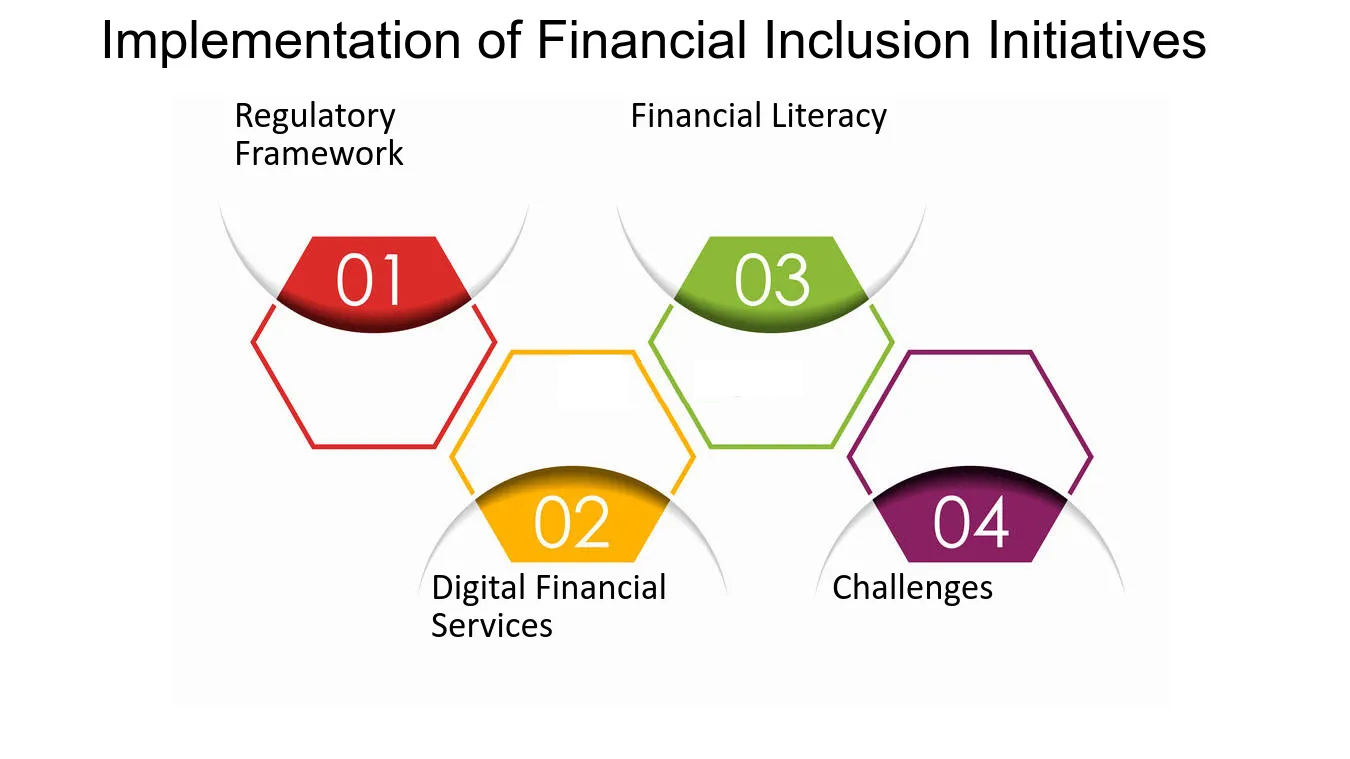
Implementation Of Financial Inclusion Initiatives
Financial inclusion aims to ensure everyone has access to and can use safe, affordable, and convenient financial services. This requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on several key pillars:
1. Regulatory Framework
- Enabling and inclusive regulations -Develop policies that favor diverse financial service providers, including fintechs, and encourage innovative solutions for unbanked and underbanked populations.
- Consumer protection -Robust regulations should ensure transparency, fair treatment, and responsible lending practices to protect users from harmful financial products or exploitation.
- Level playing field -Regulations should promote healthy competition and prevent dominance by existing institutions, fostering a diverse and innovative financial ecosystem.
2. Digital Financial Services
- Mobile money and digital wallets -Promote the use of mobile phones for financial transactions, payments, and savings, especially in unbanked areas with limited physical infrastructure.
- Digital identity infrastructure -Establishing a universal and secure digital identity system enables access to financial services without physical documentation, facilitating account opening and credit access.
- Cybersecurity and data protection -Building robust cybersecurity measures and data protection frameworks is crucial to safeguard user information and build trust in digital financial services.
3. Financial Literacy
- Financial education programs -Develop and implement age-appropriate financial education programs in schools, communities, and workplaces to build basic financial literacy skills like budgeting, saving, and responsible borrowing.
- Public awareness campaigns -Raising awareness about the benefits of financial inclusion and available financial services through targeted campaigns in local languages and mediums can encourage uptake.
- Financial counseling and support -Providing accessible financial counseling and support services can help individuals manage their finances effectively and avoid financial pitfalls.
4. Challenges
- Access to technology and infrastructure -Digital technology adoption might be limited in remote areas or for financially disadvantaged communities, requiring tailored solutions and bridging the digital divide.
- Lack of financial literacy -Low financial literacy levels can lead to poor financial decisions and inhibit full utilization of financial services.
- Regulatory hurdles -Complex or outdated regulations can hinder innovation and limit access to diverse financial service providers.
- Consumer trust and awareness -Building trust and awareness about financial services, especially digital solutions, is crucial for widespread adoption.
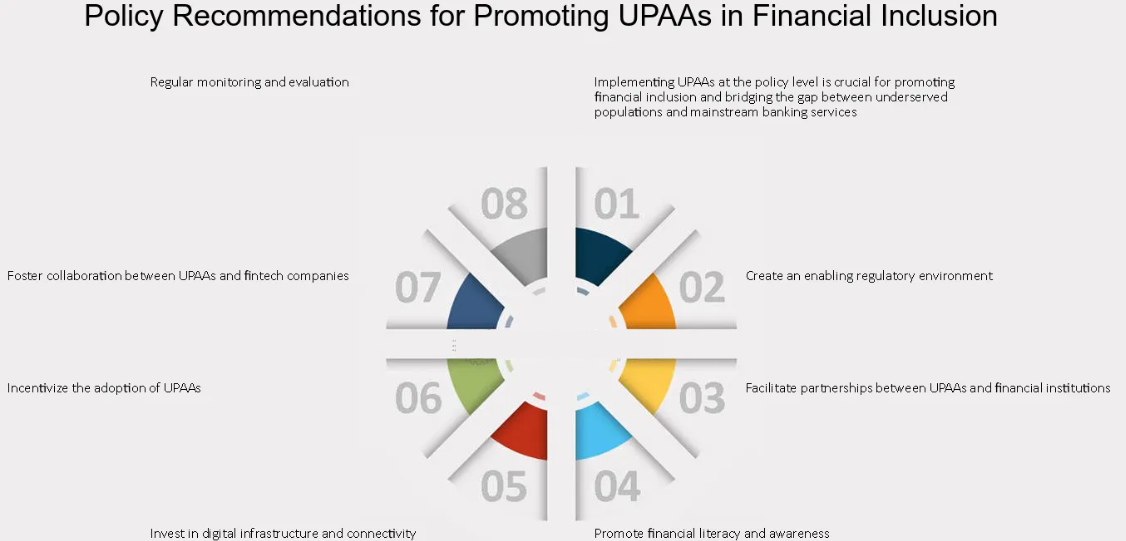
Policy Recommendations For Promoting UPAAs In Financial Inclusion
1. Accessibility
- Simplify account opening -Minimize KYC and account opening requirements, encouraging informal accounts through digital onboarding for the underbanked.
- Promote agent banking -Expand agent networks in rural areas and underbanked communities, providing physical access to UPAAs.
- Leverage alternative data sources -Use mobile phone data, utility bills, or transaction history to build creditworthiness profiles for individuals without formal financial records.
2. Reduced Transaction Costs
- Government subsidies -Provide temporary subsidies for transaction fees or merchant commissions to incentivize UPAA adoption.
- Interoperable platforms -Encourage open and interoperable UPAA platforms to foster competition and drive down transaction costs.
- Regulatory measures -Consider tax breaks or incentives for financial institutions offering affordable UPAAs.
3. Security And Transparency
- Robust consumer protection regulations -Implement clear and transparent rules on fees, data privacy, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Cybersecurity best practices -Promote strong cybersecurity measures and data protection frameworks to safeguard user information.
- Financial literacy initiatives -Educate users about UPAA features, risks, and responsible use to build trust and prevent misuse.
4. Faster Processing
- Invest in real-time payment infrastructure -Upgrade payment systems to enable instant transactions and faster access to funds.
- Streamline dispute resolution processes -Implement efficient mechanisms for resolving transaction issues and fraud prevention.
- Promote paperless transactions -Encourage digital payments and e-receipts to expedite processing and reduce reliance on physical documentation.
5. Financial Inclusion Initiatives
- Target underbanked populations -Tailor UPAA products and services to the specific needs and challenges of unbanked and underbanked communities.
- Community outreach and education -Collaborate with NGOs and community organizations to raise awareness about UPAAs and their benefits.
- Incentivize UPAA usage -Offer rewards or cashback programs for using UPAAs to promote active usage and financial inclusion.
6. Global Remittances
- Reduce remittance fees -Encourage regulatory frameworks and partnerships to lower remittance costs for migrant workers sending money home.
- Interoperability with UPAAs -Enable seamless integration of UPAAs with international remittance systems, simplifying and reducing costs for recipients.
- Promote UPAA use for cross-border transactions -Educate users about the benefits of using UPAAs for receiving remittances, fostering financial inclusion and access to formal financial services.
Achieving Sustainable Development Goals Through Financial Inclusion
The ambitious pursuit of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) hinges on a crucial element: financial inclusion. By ensuring everyone has access to affordable and appropriate financial products and services, we unlock a pathway to economic prosperity, poverty reduction, and a sustainable future.
This is where financial institutions come in, playing a pivotal role in bridging the gap and empowering individuals and communities.
Empowering People, Evolving Economies
- Breaking the Poverty Cycle -Financial inclusion equips individuals with tools to manage their finances effectively, build savings, and seize economic opportunities. This translates to improved financial stability, increased income, and a path out of poverty, leading to a more just and equitable society.
- Fueling Inclusive Growth -Small businesses and entrepreneurs, the backbone of many economies, thrive on access to financing. Financial inclusion fuels their growth, enabling them to invest, create jobs, and contribute to robust and sustainable economic development, benefiting everyone.
- Investing in a Green Future -Environmental sustainability isn't just a slogan; it's a necessity. Financial inclusion allows individuals and communities to access financial services that support green initiatives, like renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable agriculture, paving the way for a healthier planet for generations to come.
- Reaching the Underserved -Often left behind, women, rural communities, and marginalized groups can gain immense benefits from financial inclusion. Initiatives like Bangladesh's bKash mobile financial service demonstrate how access to financial tools empowers these communities, promoting economic participation and social progress.
Bridging The Gaps, Building The Future
Despite the undeniable benefits, challenges remain. Limited financial literacy, inadequate infrastructure, and restrictive regulations can hinder progress. We need to:
- Invest in financial literacy programs -Equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills to make informed financial decisions is crucial.
- Expand financial infrastructure -Reaching remote areas and underserved communities requires innovative solutions and infrastructure development.
- Streamline regulations -Fostering a regulatory environment that encourages healthy competition and diverse financial service providers is key.
The Role Of UST In Promoting Financial Inclusion
Financial inclusion, ensuring everyone has access to essential financial services, is at the heart of the United States Treasury's (UST) mission. By fostering a more inclusive financial system, the UST empowers individuals and businesses, particularly those who have traditionally faced barriers, to participate fully in the economy and improve their financial well-being.
1. Opening Doors To Banking
One key focus is ensuring everyone has access to banking services. Initiatives like Bank On encourage banks to offer low-cost accounts to those who might not meet traditional requirements. This has brought safe and affordable banking to millions previously unbanked.
2. Fueling Small Business Growth
Recognizing the crucial role small businesses play, the UST empowers them through initiatives like the Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFI) Fund. This fund provides financial assistance and technical support to CDFIs, specialized institutions serving underserved communities. By facilitating access to capital and expertise, the CDFI Fund fosters small business growth and strengthens financial inclusion.
3. Equipping With Financial Knowledge
Financial education is key to informed decisions and successful financial inclusion. The UST actively promotes initiatives like MyMoney.gov, a comprehensive online resource for budgeting, saving, investing, and other financial topics. Collaborations with various organizations further deliver tailored financial education programs to specific communities.
4. Beyond Banking - Affordable Homes For All
The UST's commitment goes beyond traditional banking. Programs like the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) leverage private investment to create millions of affordable housing units. This ensures individuals and families have access to safe and secure housing options, regardless of their income level.
5. Moving Forward - Building A More Inclusive Future
To further strengthen financial inclusion, here are some additional strategies:
- Collaboration -Work with community organizations and financial institutions to develop tailored products and services for underserved populations.
- Tech-Powered Solutions -Leverage technology and digital platforms to provide convenient and accessible financial services, especially in remote and underserved areas.
- Strategic Partnerships -Foster partnerships between government agencies, private entities, and non-profit organizations to maximize resources and expertise.
- Continuous Evaluation -Regularly assess and refine financial inclusion initiatives to ensure effectiveness and address emerging challenges.
The Future Of Financial Inclusion In Lion Economies
As we peek into the future of financial inclusion in Lion economies, a vibrant panorama unfolds. Technology, policy, and collaboration weave a tapestry of promising possibilities, empowering citizens and bridging the financial access gap.
Mobile technology stands as a shining beacon, illuminating remote areas and guiding the unbanked towards financial services. Kenya's M-Pesa exemplifies this, a mobile payment pioneer that transformed lives and bolstered inclusion rates. This trend, far from a singular spark, ignites a global revolution, urging us to consider:
1. Blockchain - Trust And Efficiency Reforged
Blockchain technology, the secure and transparent ledger, holds immense potential for financial inclusion. Digital identities crafted on its bedrock can streamline KYC processes, minimize fraud, and bolster trust in the system. Imagine individuals in remote villages, empowered by blockchain-forged identities, confidently accessing financial services once out of reach.
2. Policy - Paving The Way For Access
Governments hold the power to shape the path of financial inclusion. India's Jan Dhan Yojana scheme, a testament to this transformative potential, has ushered in a wave of bank accounts and financial accessibility. As policy evolves, embracing innovation and inclusivity, it paves the way for a brighter future.
3. Collaboration - Catalyzing Change
When banks, fintech companies, and other financial institutions join hands, the impact on inclusion multiplies. Nigeria's collaborative efforts, where government and fintechs synergize, foster a nurturing environment for initiatives that uplift and empower.
See Also:
FAQ's About Financial Inclusion Initiatives
How Can I Get Involved In Supporting Financial Inclusion?
- Educate yourself -Learn about financial inclusion and its importance.
- Support organizations -Donate to or volunteer with organizations working on financial inclusion initiatives.
- Advocate for change -Speak up for policies that promote financial inclusion and hold financial institutions accountable.
- Use responsible financial products -Choose banks and financial service providers that offer fair and transparent services.
What Is The Financial Inclusion Strategy?
The Financial Inclusion report outlines the government's progress to tackle financial exclusion over the last year and to ensure that all individuals, regardless of their background or income, have access to useful and affordable financial products and services.
What Is The Aim Of Financial Inclusion?
Financial inclusion aims to bring in digital financial solutions for the economically underprivileged people of the nation. It also intends to bring in mobile banking or financial services in order to reach the poorest people living in extremely remote areas of the country.
Conclusion
The future of financial inclusion initiatives, in Lion economies pulsates with the promise of technology, policy, and collaboration. By harnessing these powerful forces, we can weave a financial system that truly embraces everyone, leaving no individual stranded on the shores of exclusion. This endeavor, however, demands a concerted effort, a united cry for financial inclusion that echoes across continents, empowering and transforming lives in its wake.
Jump to
What Is Financial Inclusion?
Examples Of Financial Inclusion Initiatives
Implementation Of Financial Inclusion Initiatives
Policy Recommendations For Promoting UPAAs In Financial Inclusion
Achieving Sustainable Development Goals Through Financial Inclusion
The Role Of UST In Promoting Financial Inclusion
The Future Of Financial Inclusion In Lion Economies
FAQ's About Financial Inclusion Initiatives
Conclusion

Luqman Jackson
Author

Liam Evans
Reviewer
Latest Articles
Popular Articles