Can Vaping Cause Cancer? Cloudy Controversy
Explore the latest insights and research on the question: Can vaping cause cancer?Uncover the truth about vaping and its potential link to cancer risks. Stay informed and make empowered decisions about your health.
Author:Karan EmeryReviewer:Katharine TateNov 17, 202312.6K Shares293.5K Views

In recent years, the rising popularity of vaping has sparked concerns about its potential health implications, particularly regarding the possibility of causing cancer. As more individuals turn to e-cigarettes as an alternative to traditional smoking, the question lingers - can vaping cause cancer?
This exploration aims to navigate the evolving landscape of scientific studies, shedding light on the current understanding of whether vaping poses a credible threat to our cellular health and the development of cancer. As researchers delve into this critical intersection of technology and public health, it becomes paramount to dissect the available evidence and its implications for individuals seeking clarity on the risks associated with vaping.
What Is Vaping?
Vaping refers to the act of inhaling and exhaling aerosol, commonly known as vapor, produced by an electronic cigarette or similar device. Unlike traditional cigarettes that rely on combustion to deliver nicotine, vaping devices use battery-powered heating elements to vaporize a liquid, typically called e-liquid or vape juice.
The e-liquid usually contains a mix of ingredients, including nicotine, flavorings, and a base liquid, often propylene glycol or vegetable glycerin. As the liquid is heated, it transforms into an aerosol that is inhaled into the lungs. The appeal of vaping lies in its smokeless nature and the variety of available flavors, catering to different preferences.
While vaping is often promoted as a potentially less harmful alternative to smoking traditional cigarettes, concerns have emerged regarding its health effects, particularly among non-smokers and youth. The complex interplay of chemicals in e-liquids and the potential long-term consequences of inhaling these substances are subjects of ongoing research.
Vaping has evolved into a cultural phenomenon with a diverse range of devices and flavors on the market. Understanding the basics of vaping is essential for those considering its use or for individuals seeking information about this modern form of tobacco consumption.
What Happens When You Vape?
Vaping, the act of inhaling and exhaling aerosolized substances produced by electronic cigarettes, involves a complex interplay of chemicals and physiological responses. Understanding can vaping cause cancer is essential for individuals contemplating or currently engaging in this practice.
- Inhalation of Aerosolized Substances - When a person takes a puff from a vaping device, the battery-powered heating element vaporizes the e-liquid, typically containing nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals. The resulting aerosol, often referred to as vapor, is inhaled into the lungs.
- Nicotine Absorption - Nicotine, a highly addictive stimulant, is a key component of many vaping products. Upon inhalation, nicotine is rapidly absorbed through the lungs into the bloodstream, reaching the brain within seconds. This process triggers the release of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, leading to a pleasurable sensation and reinforcing the addictive nature of nicotine.
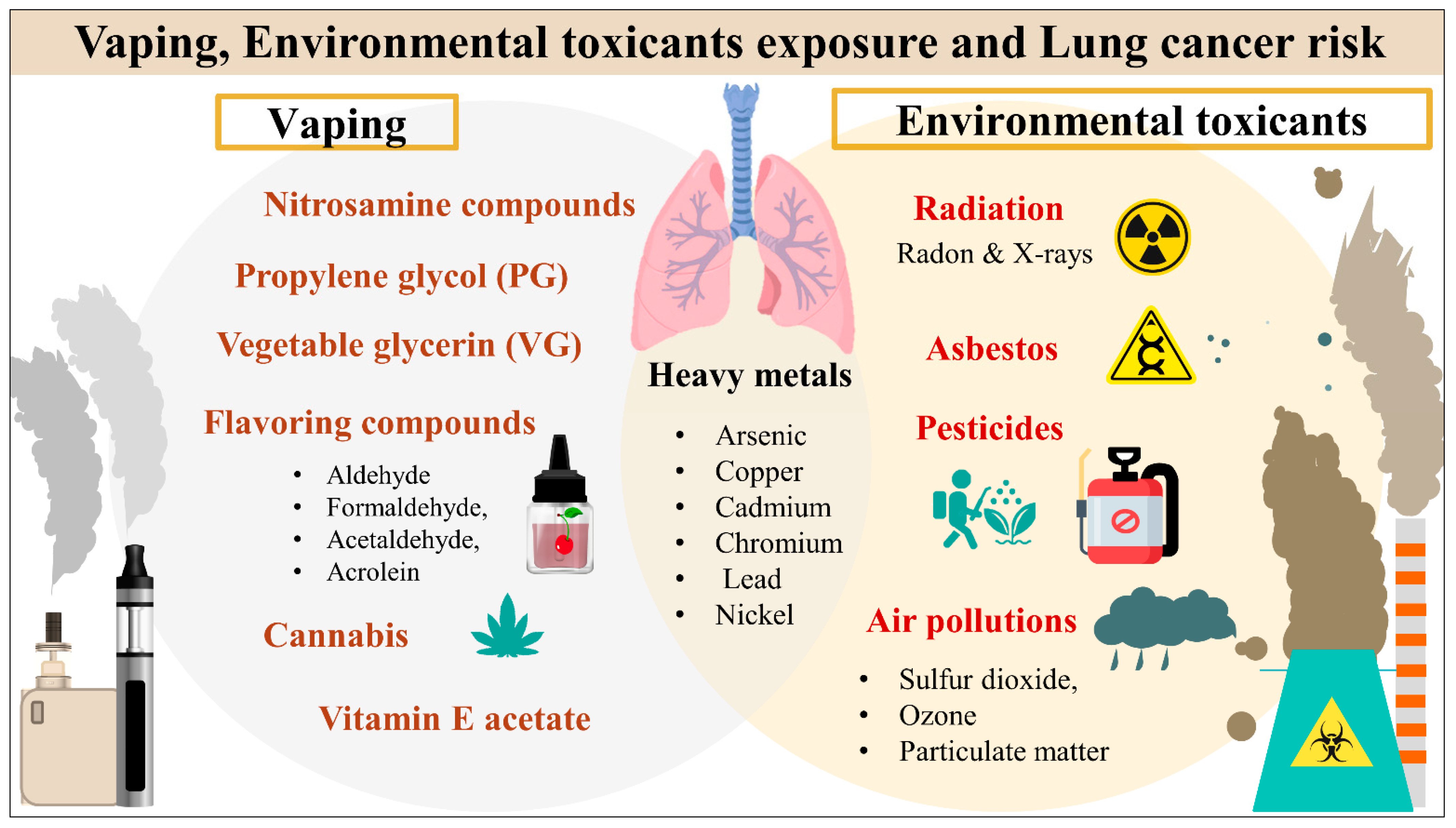
Chemicals You Inhale When Vaping
Vaping coats lungs with potentially dangerous substances rather than bathing them in a therapeutic mist, as a nebulizer does. E-liquid concoctions are often made up of a combination of flavorings, aromatic compounds, and nicotine or THC (the chemical in marijuana that induces psychological affects), all dissolved in an oily liquid basis.
The chemical under investigation is vitamin E. It's frequently used in e-liquid as a thickener and delivery agent. While it is harmless when taken orally as a supplement or applied to the skin, it is likely to be irritating when inhaled. It has been discovered in the lungs of persons who have suffered significant vaping-related harm.
Other common chemicals contained in e-liquid or created when heated may also be harmful to the lungs. These are some examples:
- Diacetyl- This culinary ingredient, which is used to enhance the flavor of e-cigarettes, has been linked to lung injury in small passageways.
- Formaldehyde- This carcinogenic substance can harm the lungs and contribute to heart disease.
- Acrolein- Commonly employed as a weed killer, this chemical can also cause lung harm.
Comparing Smoking And Vaping - Cancer Risks Explored
In the ongoing discourse surrounding smoking and vaping, a crucial aspect under scrutiny is the comparative cancer risks associated with these two distinct forms of tobacco consumption.
Traditional smoking has long been established as a leading cause of various cancers, prompting a surge in interest in vaping as a potential harm reduction alternative. Scientific studies are pivotal in unraveling the complexities of these health risks and guiding public health policies.
Cigarette smoke contains a myriad of harmful chemicals, many of which are known carcinogens that can lead to lung, throat, and other cancers. Vaping, on the other hand, involves inhaling an aerosolized mixture of substances, typically including nicotine, flavorings, and other additives.
While vaping is generally considered less harmful than smoking due to the absence of combustion and reduced exposure to harmful chemicals, it is not without its own set of health concerns.
Research endeavors in this domain often involve extensive analyses of biological samples, examining cellular responses to the byproducts of smoking and vaping.
The focus extends beyond merely identifying the presence of harmful substances to understanding how these substances interact with cells and genetic material, potentially contributing to the development of cancer.
Comparative studies aim to elucidate the specific mechanisms through which smoking and vaping may influence cancer risk differently. Researchers assess factors such as the types and concentrations of chemicals, as well as the duration and intensity of exposure.
As these studies progress, a nuanced understanding of the relative risks associated with smoking and vaping is emerging, providing valuable information for both healthcare professionals and the general public.
While vaping may present a potentially less harmful alternative to traditional smoking, the overall risk landscape is dynamic and subject to ongoing research.
Public health strategies must remain adaptable to new findings to ensure the most effective harm reduction measures are implemented, protecting individuals from the severe health consequences associated with tobacco use.
Possible Health Problems From Vaping
In recent years, the surge in popularity of vaping has prompted growing concerns about its potential impact on health. While often marketed as a safer alternative to traditional smoking, there is a need to delve into the potential health problems associated with vaping.
Respiratory Health Concerns
One prominent area of focus in the study of vaping-related health problems is the impact on respiratory health. The inhalation of aerosols produced by e-cigarettes introduces various substances, including potentially harmful chemicals, into the lungs.
Research is ongoing to assess the long-term consequences of these exposures, examining potential links to respiratory issues such as chronic bronchitis and impaired lung function.
Cardiovascular Risks
Nicotine, a common component in many vaping products, raises concerns about cardiovascular health. Nicotine is known to elevate heart rate and blood pressure, potentially increasing the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Studies are exploring the relationship between vaping and an elevated risk of heart disease, especially in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
Chemical Exposures And Toxicity
Vaping liquids often contain a mix of chemicals beyond nicotine, including flavorings and other additives. The inhalation of these substances may pose risks of chemical exposures and toxicity.
Understanding the potential harm from these chemicals and their effects on various organ systems is a crucial aspect of evaluating health risks associated with vaping.
- Teenagers' brain development may be harmed by nicotine.
- Low birth weight and early delivery might result from using nicotine during pregnancy.
- When present in high concentrations, propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin can irritate the lungs and airways.
- Some e-cigarettes might have volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can harm the liver, kidneys, and neurological system in addition to irritating the eyes, nose, and throat, producing headaches and nausea.
- Diacetyl, a flavoring used in some e-cigarettes, has the potential to induce bronchiolitis obliterans, a serious lung condition.
- Vape e-liquid that is not heated properly can produce formaldehyde, a carcinogen.
Addiction And Behavioral Health
Nicotine's addictive properties are a well-established concern in the realm of tobacco use. Vaping's role in sustaining or even exacerbating nicotine addiction is a significant health consideration.
Additionally, the behavioral aspects of vaping, such as its appeal to non-smokers and younger populations, raise questions about the potential for addiction and its broader impact on mental health.
As the landscape of vaping-related health research continues to evolve, understanding the potential health problems associated with vaping is critical. Comprehensive studies across various health domains are essential for informing public health policies and empowering individuals to make informed choices about their well-being.
How To Quit Vaping?
Quitting vaping, like any form of tobacco use, is a challenging yet crucial journey towards better health. Whether motivated by concerns about potential health risks or a desire for a nicotine-free lifestyle, individuals looking to break free from vaping can benefit from a strategic and supportive approach.
- Acknowledge the Decision to Quit - The first step in quitting vaping is recognizing the need for change. Acknowledge the impact of vaping on your health and commit to making a positive transformation.
- Set a Quit Date - Establish a specific quit date, providing a clear target for your journey to become vape-free. This date serves as a tangible goal and can help mentally prepare for the transition.
- Seek Support - Engage with friends, family, or support groups to share your decision and seek encouragement. Having a support system is invaluable during challenging moments and can provide accountability throughout the quitting process.
- Gradual Reduction - Consider a gradual reduction approach where you slowly decrease the nicotine levels in your e-liquid or extend the time between vaping sessions. This method can help ease the transition and minimize withdrawal symptoms.
- Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) - Explore the use of nicotine replacement therapy, such as nicotine patches, gum, or lozenges, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. These aids can help manage cravings during the quitting process.
- Identify Triggers and Develop Coping Strategies - Recognize situations, emotions, or activities that trigger the urge to vape. Develop alternative coping strategies, such as deep breathing, exercise, or engaging in a hobby, to redirect your focus during these moments.
- Professional Guidance - Consult with healthcare professionals or join cessation programs to receive expert guidance and personalized strategies for quitting. Professionals can offer tailored advice based on your individual needs.
- Stay Positive and Persistent - Quitting vaping is a journey that may involve setbacks. Stay positive, celebrate small victories, and persist through challenges. Understand that progress is gradual, and every step toward a vape-free life is a significant achievement.
- Celebrate Milestones - Celebrate milestones, whether it's a week, a month, or more without vaping. Rewarding yourself for your achievements can reinforce your commitment to a vape-free lifestyle.
- Establish Healthy Habits - Replace vaping with healthy habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress-reducing activities. Building a healthier lifestyle can contribute to the overall success of quitting vaping.
- Remember, quitting vaping is a personal journey, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Tailor your strategy to your unique circumstances, and don't hesitate to seek professional support to increase your chances of success on the path to a vape-free life.
Can Vaping Cause Cancer? - FAQs
What Chemicals In E-cigarettes May Contribute To Cancer?
E-cigarettes contain various chemicals, including nicotine and potentially harmful substances. Some studies suggest that certain chemicals in e-cigarettes may have carcinogenic properties, but more research is needed for a definitive answer.
How Does Vaping Compare To Traditional Smoking In Terms Of Cancer Risk?
Vaping is generally considered less harmful than traditional smoking, but it is not without risks. Research is underway to assess the comparative cancer risks associated with vaping versus smoking.
Are There Specific Types Of Cancer Linked To Vaping?
The specific types of cancer associated with vaping are not well-established. Research is exploring potential links between vaping and various cancers, but conclusive findings are awaited.
Can Secondhand Vapor From E-cigarettes Pose A Cancer Risk?
The impact of secondhand vapor on cancer risk is an area of concern. While it is generally considered less harmful than secondhand smoke, research is ongoing to understand any potential risks.
Is There A Safe Level Of Vaping That Does Not Pose A Cancer Risk?
Determining a safe level of vaping is challenging, as individual responses to e-cigarette use vary. Health experts emphasize the importance of minimizing exposure to potentially harmful substances.
Conclusion
Can vaping cause cancer? The relationship between vaping and cancer is a complex and evolving area of study. While some research suggests potential risks, the long-term effects of vaping on cancer development remain inconclusive.
It is imperative for individuals, policymakers, and healthcare professionals to stay informed about the latest scientific findings to make well-informed decisions about the use of e-cigarettes. As the scientific community continues to explore this issue, responsible vaping practices and a cautious approach are crucial in safeguarding public health.

Karan Emery
Author

Katharine Tate
Reviewer
Latest Articles
Popular Articles