Bitcoin Forks - The Roadmap To Understanding
Explore Bitcoin forks: types, implications, and notable examples in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Author:Camilo WoodReviewer:Stefano MclaughlinFeb 06, 20245K Shares113.6K Views

Bitcoin forksare significant events in the cryptocurrency ecosystem that can have profound implications for users, developers, and investors. A fork occurs when a blockchain diverges into two separate paths, resulting in the creation of a new cryptocurrency based on the original protocol.
These forks can be classified into two main types: hard forks and soft forks. In this discussion, we'll explore the mechanics of Bitcoin forks, their implications, and some notable examples.
What Are Bitcoin Forks?
A split in the Bitcoin network that results in the creation of two distinct "branches," each with its own protocol, is known as a bitcoin fork. While one branch will stick to the pre-fork protocol, the other branch will use a new protocol with distinct guidelines.
The majority of Bitcoin forks are made to improve the network, either by making blocks bigger or by accelerating transactions. But not every Bitcoin fork is taken up right away, and the community frequently debates whether to utilize the original or new branches.
Within the cryptocurrency market, bitcoin forks are a much-discussed phenomenon that can have a big effect on all parties involved. These splits radically alter the way the network functions, how consensus is reached, and even what kind of digital money is utilized.
Owing to the quick-paced nature of the cryptocurrency industry, new technologies that can improve a blockchain's efficiency are always being created. Since Bitcoin was first developed in 2009, the network's protocol is a little out of date. It can, however, be updated and modified via this forking method.
It's important to remember that any "branch" created by the split will still adhere to the fundamental principles of the original blockchain, in this example, the Bitcoin network. Despite their differences, the branches frequently follow the original design of Bitcoin, albeit with a few significant modifications.
Hard Forks Vs. Soft Forks
A hard fork occurs when a blockchain protocol undergoes a fundamental change that is not compatible with previous versions. This change results in a permanent split, creating two separate chains with distinct protocols and transaction histories. Examples of hard forks include Bitcoin Cash (BCH) and Bitcoin SV (BSV), both of which split from the original Bitcoin blockchain in 2017.
On the other hand, a soft fork is a backward-compatible upgrade to the blockchain protocol. In a soft fork, only a subset of network nodes need to upgrade to the new protocol, maintaining consensus across the network. Segregated Witness (SegWit) is an example of a soft fork implemented on the Bitcoin blockchain in 2017 to increase transaction capacity and enhance scalability.
Implications Of Bitcoin Forks
Bitcoin forks have several implications for the cryptocurrency ecosystem:
- Creation of New Cryptocurrencies -The primary outcome of a fork is the creation of a new cryptocurrency with its own unique features, branding, and community. Bitcoin Cash, for example, was created to address scalability issues by increasing the block size limit, while Bitcoin SV aimed to restore the original Bitcoin protocol's vision of large blocks and low fees.
- Community Divisions -Forks often result from disagreements within the community regarding the direction of the protocol. These disagreements can lead to divisions among developers, miners, and users, creating rifts that may persist long after the fork has occurred.
- Market Dynamics -Forks can impact the value and market dynamics of both the original cryptocurrency and the newly created coins. In some cases, the value of the original cryptocurrency may decline as investors flock to the new coin, seeking potential profits or aligning with the vision of the forked project.
- Security Concerns -Forks can introduce security vulnerabilities and risks, particularly if they result in a contentious split or if the new cryptocurrency lacks sufficient support from developers and miners. Users must exercise caution when transacting or holding coins on newly forked chains to avoid potential losses or security breaches.
- Innovation and Experimentation -Despite the challenges posed by forks, they also serve as a mechanism for innovation and experimentation within the cryptocurrency space. Forked projects may introduce novel features, governance models, or consensus mechanisms that contribute to the evolution of blockchain technology.
The Negative Aspects Of Bitcoin Splits
Back in 2017, when Bitcoin Cash kicked off the forking craze, it appeared that expressing dissatisfaction with the direction that Bitcoin was going in was acceptable through forking.
Since then, though, forks have tended to resemble one another rather than diverge, and it appears that marketing rather than genuine doctrine was the driving force behind their creation.
In other words, there's no need to produce a Bitcoin clone if someone believes they can make a coin that is superior to Bitcoin, they can just build a whole new altcoin instead. In my view, given the current state of affairs, developers choose to split Bitcoin for three primary reasons:
Fast Cash For Developers
Not all of these forks are exact replicas of Bitcoin's past. Developers now receive an initial big supply of the new coin, which they can dump onto the market as soon as it begins trading, thanks to changes made to the rules.
Stated differently, the creators had the option to create a new cryptocurrency entirely, but they chose to diverge from Bitcoin in order to generate a substantial amount of initial hype and value.
Scams
A few forks have emerged, including Simply said, Bitcoin Platinum is a hoax. Forks designed to shorten the price of Bitcoin (such as Bitcoin Platinum) or more complex ones that steal users' actual Bitcoins while they claim the new coin (like in the case of False Bitcoin Gold wallet) are examples of scams.
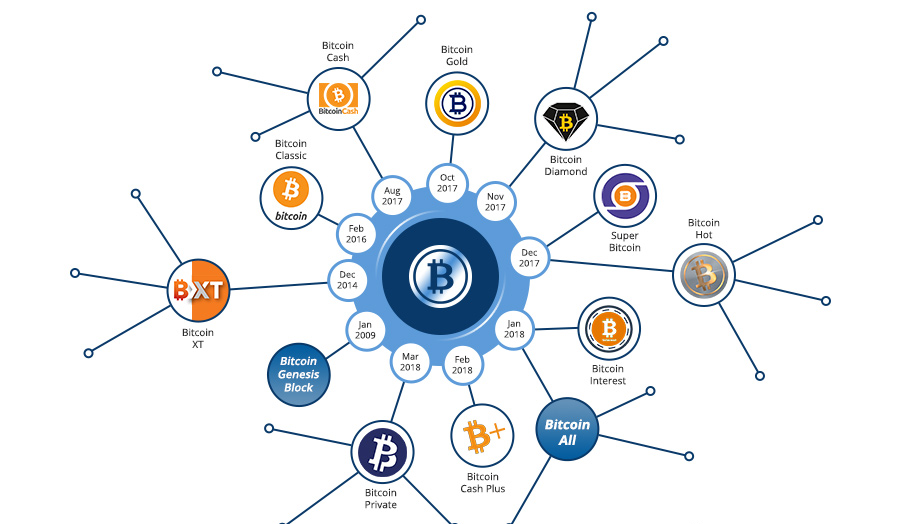
List Of The Main Bitcoin Forks
- Bitcoin XT -Introduced by Mike Hearn in late 2014, this was the first significant hard fork to the Bitcoin software. The goal of Bitcoin XT was to boost transaction volume from 7 to 24 per second. Although the fork was successful at first, users gradually stopped caring about it and gave up on it.
- Bitcoin Classic - After Bitcoin XT was shelved, Bitcoin Classic was introduced with the same intent. Instead of Hearn's suggested 8 MB, a hard fork resulted in a 2 MB block size increase. The majority of the community has moved on to other branches, although the project is still active.
- Bitcoin Unlimited -When Bitcoin Unlimited was first announced at the beginning of 2016, its creators did not specify the kind of fork that would be necessary. The size of blocks is left up to the miners, with a 16 megabyte cap. It had attracted some interest, but it was not well received.
- Segregated Witness (SegWit) -It sought to make each bitcoin transaction smaller in order to facilitate many transactions at once. In order to prevent rogue nodes from altering transaction information, it also attempted to decrease transaction malleability. Though Segregated Witness was more of a soft fork (software update), it might have been the catalyst for some of the hard forks in Bitcoin history.
- Bitcoin Cash -A few developers and users of Bitcoin desired to forego the improvements that SegWit brought about. They therefore produced Bitcoin Cash, a hard fork. In August 2017, the fork separated from the main blockchain. With the support of numerous well-known people, it is one of the most successful forks. With a price above $300, Bitcoin Cash is currently the 25th-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization.
Bitcoin Forks - FAQs
What Is A Bitcoin Fork And How Does It Occur?
A Bitcoin fork is a divergence in the blockchain's protocol, resulting in two separate chains. It occurs when miners and developers disagree on proposed changes to the protocol.
What Are The Main Types Of Bitcoin Forks?
The main types of Bitcoin forks are hard forks and soft forks. Hard forks result in a permanent split, creating two separate chains, while soft forks are backward-compatible upgrades to the protocol.
How Do Bitcoin Forks Impact The Value Of The Original Cryptocurrency And The Newly Created Coins?
Bitcoin forks can impact the value of both the original cryptocurrency and the newly created coins, with investors often speculating on the potential value and adoption of the forked coins.
How Do Users Safeguard Their Assets During A Bitcoin Fork?
Users should exercise caution when transacting or holding coins during a Bitcoin fork to avoid potential losses or security breaches. It's essential to follow best practices and use reputable wallets and exchanges.
How Many Times Has Bitcoin Been Forked?
Since its launch, there have been more than 100 hard forks in Bitcoin. Forks aim to enhance a blockchain's functionality or address issues.
What Role Do Developers Play In Bitcoin Forks?
Developers play a crucial role in proposing and implementing changes to the Bitcoin protocol. Forks often result from disagreements among developers regarding proposed upgrades or changes to the protocol.
Will Bitcoin Fork Again?
As of right now, there isn't any thorough or trustworthy information available on the impending Bitcoin network fork.
Conclusion
Bitcoin forks are integral to the dynamic nature of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, providing opportunities for innovation, experimentation, and community engagement.
While forks can result in divisions and market volatility, they also serve as a mechanism for addressing scalability issues, exploring new features, and advancing the broader adoption of blockchain technology.
As the cryptocurrency space continues to evolve, Bitcoin forks will likely remain a topic of interest and contention among stakeholders seeking to shape the future of digital finance.

Camilo Wood
Author

Stefano Mclaughlin
Reviewer
Latest Articles
Popular Articles