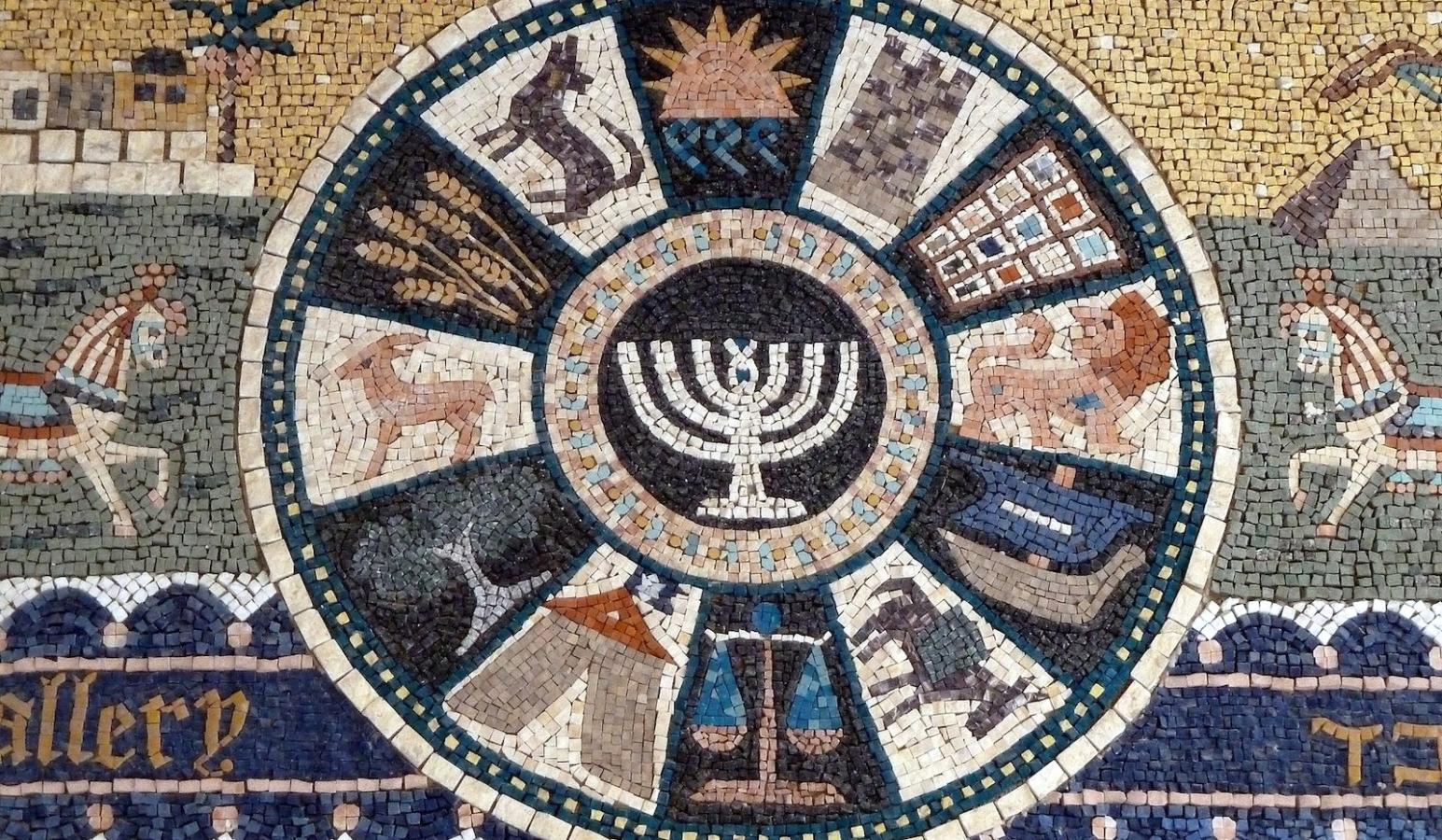
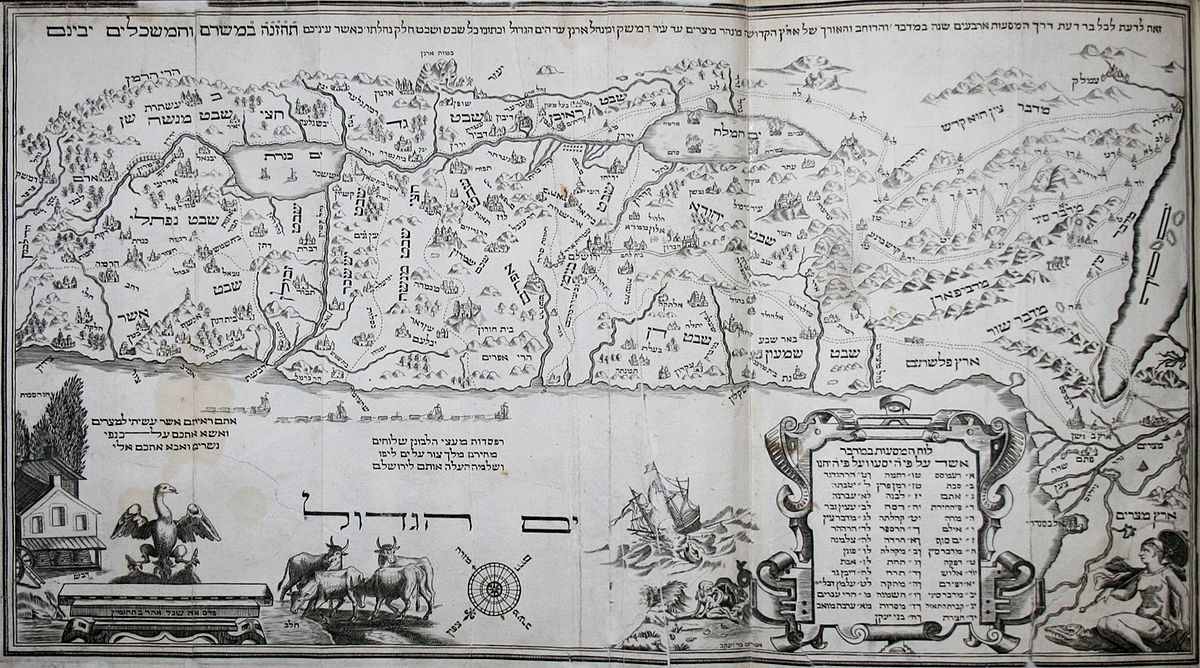
The 12 Tribes Of Israel - A Historical And Biblical Overview
The 12 Tribes of Israel hold a significant place in the history and religious beliefs of Judaism and Christianity. According to the Bible, these tribes are the descendants of the twelve sons of Jacob, who was later named Israel.
Author:Paolo ReynaReviewer:James PierceOct 12, 202310.1K Shares178.8K Views
The 12 Tribes of Israelhold a significant place in the history and religious beliefs of Judaism and Christianity. According to the Bible, these tribes are the descendants of the twelve sons of Jacob, who was later named Israel.
Each tribe has its own unique characteristics, customs, and territories, making them a fascinating subject of study. In this article, we will explore the origins, history, and significance of the 12 Tribes of Israel.
Origins And Biblical Account Of The 12 Tribes Of Israel
The origins of the 12 Tribes of Israel are deeply rooted in the ancient scriptures of the Old Testament, specifically in the Book of Genesis. This foundational text narrates the story of Jacob, a pivotal figure in the Abrahamic tradition and the grandson of Abraham, the patriarch of Israel. Jacob had a significant role not only in the formation of the tribes but also in the shaping of the destiny of the Israelites.
Jacob's Twelve Sons - The Founding Fathers
Jacob, whose name was later changed to Israel after a divine encounter, had twelve sons: Reuben, Simeon, Levi, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, Dan, Gad, Asher, Naphtali, Joseph, and Benjamin. Each of these sons became the progenitors of the twelve tribes of Israel. The blessings and prophecies bestowed upon them by Jacob were not mere words but were believed to carry divine significance, shaping the unique identity and character of each tribe.
Distinct Communities And Divine Design
These twelve sons, in accordance with Jacob's blessings and God's plan, evolved into distinct communities, each with its own customs, territories, and roles within the larger framework of ancient Israelite society. The division of the tribes was not just a matter of convenience but was seen as a divine design, where each tribe had a specific purpose and contribution to the overall tapestry of the Israelite nation.
A Tapestry Of Diversity
The diversity among the tribes was not limited to geographical boundaries; it extended to their skills, traditions, and even their relationships with neighboring tribes and nations. This diversity was considered a strength, showcasing the multifaceted nature of the Israelite heritage. The tribes, despite their differences, shared a common lineage and a collective destiny, symbolizing the unity amidst diversity that characterized the ancient Israelite society.
Division Of The Land - Fulfilling The Promise
The pivotal moment in the history of the 12 Tribes of Israel occurred after their miraculous liberation from the bondage of Egyptunder the leadership of Moses. Guided by divine providence and the promise of a land flowing with milk and honey, the Israelites embarked on a monumental journey toward the Promised Land.
The Exodus
The Exodus, a defining episode in the Israelite narrative, symbolized not just a physical exodus from Egypt but also a spiritual liberation. Enduring harsh conditions and divine trials, the Israelites, like a united nation under God's guidance, traversed the wilderness. Their faith and resilience were their guiding lights, shaping them into a community bound by a shared history and a shared destiny.
Arrival In The Promised Land
Upon reaching the borders of the Promised Land, it was Joshua, Moses' successor, who led the tribes into this land of divine promise. This event marked the culmination of generations of anticipation and faith. The land, described as a place flowing with milk and honey, was not merely a geographical location; it was a manifestation of God's covenant with the descendants of Abraham.
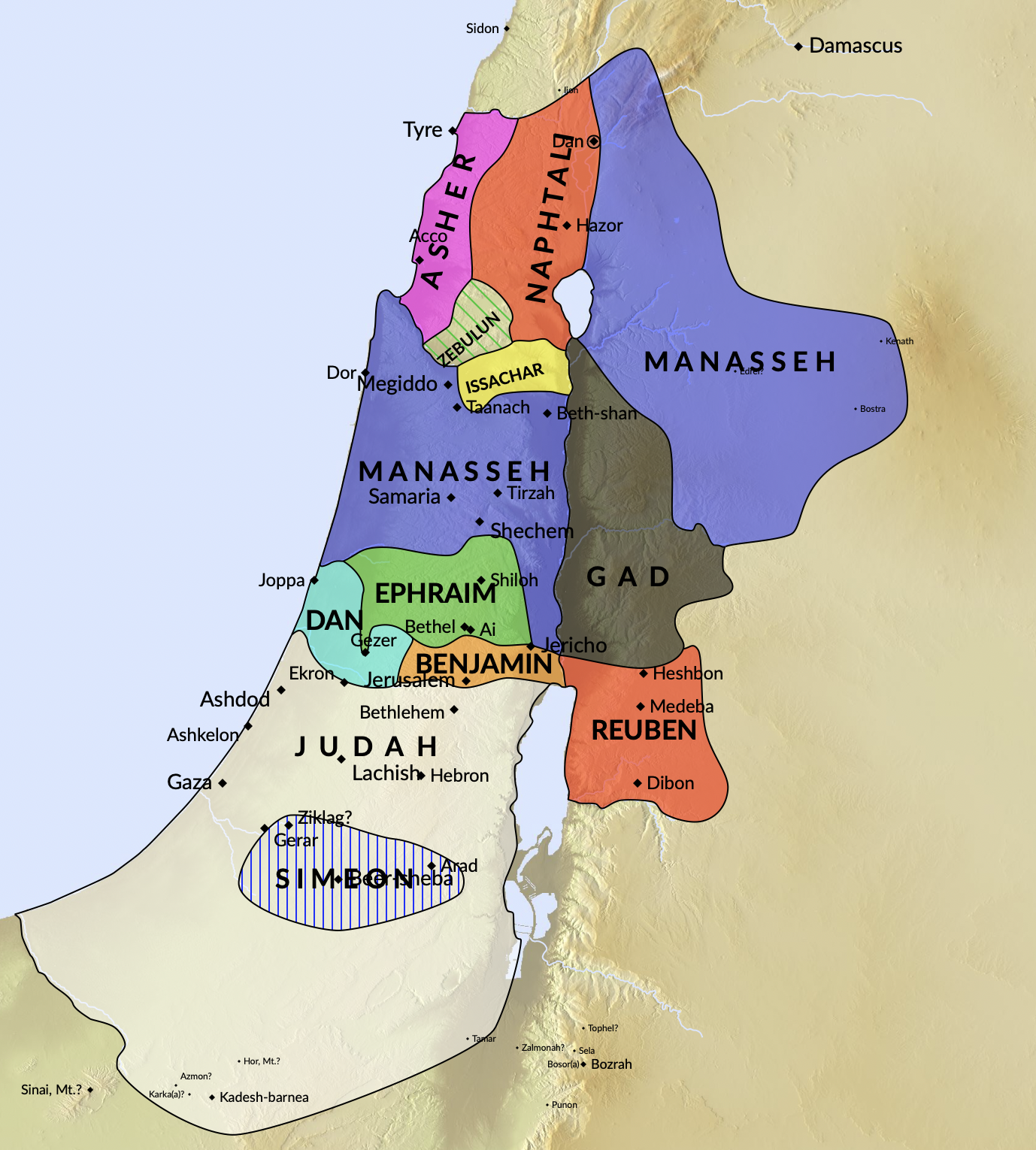
Detailed Allotment
The division of the land among the twelve tribes was a meticulous process outlined in the book of Joshua. This division was not a random allocation of territory; it was a carefully orchestrated plan reflecting God’s promise fulfilled.Each tribe received its designated portion, strategically located based on various factors such as resources, geographical features, and, perhaps most importantly, divine providence.
God’s Promise To Abraham Fulfilled
This division of the land was not just a political or administrative act; it was the realization of God's covenant with Abraham. The land, apportioned among the tribes, signified their inheritance, a tangible symbol of their status as God’s chosen people. The fulfillment of this promise represented divine faithfulness and established a profound connection between the people and their Creator.
The Twelve Sons - Foundation Of The Tribes
The twelve sons of Jacob, as listed in the order from oldest to youngest—Reuben, Simeon, Levi, Judah, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Issachar, Zebulun, Joseph, and Benjamin—form the very bedrock upon which the twelve tribes of Israel were established. Their individual stories and the blessings bestowed upon them by their father Jacob played a significant role in shaping the destiny of the Israelite nation.
1. Reuben - The Eldest Son
Reuben, as the eldest son, held a position of prominence within the family. However, due to certain circumstances, his birthright was eventually transferred to Joseph, the first son of Jacob's beloved wife Rachel.
2. Simeon And 3. Levi - Brothers In Unity
Simeon and Levi were known for their fierce loyalty to their sister Dinah. Their actions, although driven by protective instincts, led to a complex series of events, showcasing the intricate family dynamics within the tribe.
4. Judah - The Royal Lineage
Judah, the fourth son, played a pivotal role in the lineage of Israel's future kings, most notably King David. He became a symbol of leadership and strength, exemplifying the tribe's importance in the nation's political landscape.
5. Dan, 6. Naphtali, 7. Gad, And 8. Asher - Diverse Territories
These sons were instrumental in expanding the geographical reach of the tribes. Dan's descendants settled in the coastal region, while Naphtali's tribe occupied the northern parts. Gad and Asher, too, found their places in distinct territories, contributing to the varied landscape of ancient Israel.
9. Issachar, 10. Zebulun - Agricultural Prosperity
Issachar and Zebulun were associated with agricultural abundance. Their territories were blessed with fertile lands, emphasizing the importance of agriculture in the sustenance and growth of the tribes.
11. Joseph - A Tale Of Redemption And Prosperity
Joseph, despite being sold into slavery by his brothers, rose to prominence in Egypt, eventually reuniting with his family. His descendants, Ephraim and Manasseh, were adopted by Jacob, receiving equal status as his own sons and forming separate tribes within Israel.
12. Benjamin - The Beloved Son
Benjamin, the youngest, was the beloved child of Jacob and Rachel. His tribe occupied a strategic location near Jerusalem, and their unity with Judah played a crucial role in the history of Israel.
Legacy And Lessons
The legacy of the tribes extends far beyond ancient history. It teaches us the value of recognizing and honoring diverse talents and contributions within a community. It emphasizes the importance of unity and collaboration, where each individual or group, irrespective of their role, is integral to the collective progress and well-being of society.
In essence, the significance and roles of each tribe in ancient Israel serve as a timeless lesson, reminding us of the power of diversity, unity, and the harmonious interplay of distinct strengths within any society.
Historical Impact And Modern Relevance - Echoes Across Time
The 12 Tribes of Israel, although rooted in the ancient sands of history, cast a long shadow that continues to influence the world in profound ways. Their historical impact and modern relevance resonate not just in the religious spheres but also in cultural, social, and even personal dimensions.
Preservation Of Tradition And Faith
In the annals of history, the tribes' stories, customs, and laws have been meticulously preserved. They serve as the foundation upon which the world's major monotheistic religions, Judaism and Christianity, stand. These narratives offer moral guidance, ethical principles, and spiritual insights, shaping the beliefs and practices of millions.
Cultural Tapestry And Diversity
The tribes' legacy is woven into the cultural tapestry of nations worldwide. Their tales of resilience, faith, and unity inspire artists, writers, and filmmakers, becoming themes in literature, art, and cinema. The stories of bravery, loyalty, and divine intervention captivate audiences, transcending religious boundaries and offering universal lessons.
Identity And Belonging In Modern Times
In contemporary society, numerous Jewish and Christian communities identify with specific tribes, tracing their lineage back to the original twelve. This connection is more than just a historical link; it fosters a profound sense of identity and belonging among believers. The knowledge of one's ancestral tribe creates a bridge between the past and the present, strengthening the bond with a rich heritage that extends thousands of years.
Unity Amidst Diversity
The modern identification with the tribes underscores the enduring legacy of unity amidst diversity. It exemplifies the idea that despite our differences, we are all part of a larger, shared story. This recognition fosters tolerance, understanding, and respect for diverse cultures and traditions, emphasizing the fundamental principle of unity that echoes through the ages.
Inspiration And Hope
Moreover, the 12 Tribesserve as a source of inspiration and hope. They remind humanity of the power of faith, the strength of community, and the promise of divine providence. In an ever-changing world, these ancient narratives provide a stable foundation, offering solace, guidance, and reassurance to those navigating the complexities of modern life.
Explore The Rich Heritage Of The 12 Tribes Of Israel
Certainly, feeling lonely is a common human experience, and it's essential to recognize that you're not alone in feeling this way. Many people go through periods of loneliness, and it's okay to feel the way you do. If you're looking for ways to connect with others or find a sense of belonging, there are various resources and strategies available:
Social Support Networks
Consider reaching out to friends, family, or acquaintances you trust. Sometimes, opening up to someone you know can alleviate feelings of loneliness. If face-to-face interaction isn't possible, social media platforms can also provide a way to connect with others who share your interests.
Community Activities
Engaging in community activities or joining clubs related to your interests can help you meet like-minded people. Whether it's a sports club, book group, art class, or volunteer organization, participating in activities can create opportunities for meaningful social interactions.
Online Support Communities
There are numerous online forums and communities where people discuss their feelings and experiences. Websites like Reddit (such as r/lonely or r/depression) have supportive communities where you can share your thoughts and read about others' experiences.
Therapy And Counseling
Talking to a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, can provide a safe space to explore your feelings of loneliness. They can offer guidance and coping strategies tailored to your specific situation.
Mindfulness And Meditation
Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help you manage feelings of loneliness and improve your overall well-being. Apps like Headspace or Calm offer guided meditation sessions that can be done in the comfort of your home.
Hobbies And Creative Outlets
Engaging in activities you're passionate about, such as writing, painting, gardening, or playing a musical instrument, can be not only fulfilling but also provide an opportunity to connect with others who share your interests.
Local Support Hotlines
In times of distress, local hotlines or helplines can provide immediate support. These services are staffed by trained professionals who can offer a listening ear and valuable guidance.
For in-depth knowledge about the 12 Tribes of Israel, their significance, and the mystical connection with stone colors, visit Bernardine. Delve into the fascinating world of ancient traditions and explore the symbolism behind each tribe's unique stone colors.
The Lost Tribe
The concept of the 13th tribe is a topic that has intrigued historians, theologians, and scholars for centuries. In some traditions and historical texts, especially within Jewish folklore and the teachings of the Kabbalah, there is a belief in the existence of a 13th tribe alongside the original 12 Tribes of Israel. This mysterious tribe is often referred to as the "Lost Tribe of Israel."
The Mystery Of The Lost Tribe
The story of the Lost Tribe originates from the time of the Assyrian conquest of the northern kingdom of Israel in 722 BCE. It is believed that during this conquest, one of the twelve tribes was exiled or lost to history. The identity and fate of this lost tribe remain unknown, giving rise to various theories and speculations.
Historical And Theological Interpretations
Different religious and cultural groups have their interpretations regarding the 13th tribe. Some believe that this lost tribe might have assimilated into other cultures over centuries, while others speculate that they might have migrated to distant lands, leaving behind their Israelite heritage. Several groups around the world, especially in regions like Africa and Asia, have claimed to be descendants of the Lost Tribe of Israel, further adding to the mystery and intrigue.
Modern Perspectives And Research
In recent times, advances in genetics and DNA research have led to efforts to trace the ancestry of different populations, potentially shedding light on the historical movements of ancient tribes. Some genetic studies have explored the possibility of identifying the lost tribes through DNA analysis, although definitive conclusions remain elusive.
Cultural And Literary Influence
The idea of the Lost Tribe of Israel has captured the imagination of writers, filmmakers, and artists, leading to numerous works of fiction and non-fiction exploring this enigmatic theme. These literary and artistic creations have further embedded the concept of the 13th tribe into popular culture, making it a captivating subject of study and fascination.
Symbolism And Mysticism
Beyond historical and anthropological perspectives, the 13th tribe has gained symbolic significance in various spiritual and mystical traditions. In Kabbalistic teachings, the number 13 holds mystical importance, often associated with unity and divine influence. The concept of the 13th tribe is sometimes used metaphorically to represent a hidden or higher level of spiritual knowledge.
12 Tribes Of Israel - People Also Ask
What Is The 13th Tribe Of Israel?
The 13th tribe of Israel is a concept rooted in historical and religious speculation. It is often referred to as the "Lost Tribe of Israel." According to ancient texts, specifically in the context of the Assyrian conquest of the northern kingdom of Israel in 722 BCE, one of the twelve tribes was believed to have been lost or exiled. The identity and fate of this lost tribe have remained uncertain, giving rise to the idea of a 13th tribe. Various theories, folklore, and cultural claims have emerged over the centuries, but there is no conclusive historical evidence to identify the exact identity of the 13th tribe.
What Tribe Was David From?
King David of Israel, one of the most significant figures in biblical history, belonged to the Tribe of Judah. He was the youngest son of Jesse and was anointed by the prophet Samuel to be the future king of Israel. The Tribe of Judah, one of the twelve tribes of Israel, occupied a prominent place in the nation's history. David's lineage from Judah is significant because it fulfilled prophecies regarding the Messiah, including the lineage of Jesus Christ in Christian traditions.
Why Did God Reject The Tribe Of Ephraim?
In biblical narratives, the Tribe of Ephraim faced God's disapproval and punishment primarily due to their disobedience and idolatry. The tribe, descended from Joseph, the son of Jacob, was initially blessed and held a significant role among the tribes. However, Ephraim's leadership became increasingly corrupt, leading to idol worship and moral degradation.
Conclusion
The story of the 12 Tribes of Israel is a testament to faith, unity, and the fulfillment of divine promises. Through centuries of history, these tribes have left an indelible mark on the religious, cultural, and social landscapes of the world. Studying their legacy provides invaluable insights into the origins of belief systems and the shared heritage of humanity. As we continue to explore and preserve these ancient narratives, the legacy of the 12 Tribes of Israel will undoubtedly endure for generations to come.
Jump to
Origins And Biblical Account Of The 12 Tribes Of Israel
Division Of The Land - Fulfilling The Promise
The Twelve Sons - Foundation Of The Tribes
Historical Impact And Modern Relevance - Echoes Across Time
Explore The Rich Heritage Of The 12 Tribes Of Israel
The Lost Tribe
12 Tribes Of Israel - People Also Ask
Conclusion

Paolo Reyna
Author

James Pierce
Reviewer
Latest Articles
Popular Articles